python如何生成各种随机分布图
在学习生活中,我们经常性的发现有很多事物背后都有某种规律,而且,这种规律可能符合某种随机分布,比如:正态分布、对数正态分布、beta分布等等。
所以,了解某种分布对一些事物有更加深入的理解并能清楚的阐释事物的规律性。现在,用python产生一组随机数据,来演示这些分布:
import random
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
SAMPLE_SIZE = 1000
buckets = 100
fig = plt.figure()
matplotlib.rcParams.update({"font.size": 7})
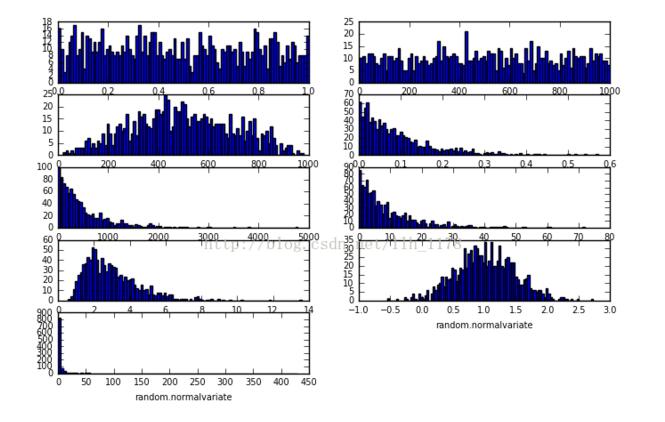
#第一个图形是在[0,1)之间分布的随机变量(normal distributed random variable)。
ax = fig.add_subplot(5,2,1)
ax.set_xlabel("random.random")
res = [random.random() for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
ax.hist(res, buckets)
#第二个图形是一个均匀分布的随机变量(uniformly distributed random variable)。
ax_2 = fig.add_subplot(5,2,2)
ax_2.set_xlabel("random.uniform")
a = 1
b = SAMPLE_SIZE
res_2 = [random.uniform(a, b) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
ax_2.hist(res_2, buckets)
#第三个图形是一个三角形分布(triangular distribution)。
ax_3 = fig.add_subplot(5,2,3)
ax_3.set_xlabel("random.triangular")
low = 1
high = SAMPLE_SIZE
res_3 = [random.uniform(low, high) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
ax_3.hist(res_3, buckets)
#第四个图形是一个beta分布(beta distribution)。参数的条件是alpha 和 beta 都要大于0, 返回值在0~1之间。
plt.subplot(5,2,4)
plt.xlabel("random.betavariate")
alpha = 1
beta = 10
res_4 = [random.betavariate(alpha, beta) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_4, buckets)
#第五个图形是一个指数分布(exponential distribution)。 lambd 的值是 1.0 除以期望的中值,是一个不为零的数(参数应该叫做lambda没但它是python的一个保留字)。如果lambd是整数,返回值的范围是零到正无穷大;如果lambd为负,返回值的范围是负无穷大到零。
plt.subplot(5,2,5)
plt.xlabel("random.expovariate")
lambd = 1.0/ ((SAMPLE_SIZE + 1) / 2.)
res_5 = [random.expovariate(lambd) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_5, buckets)
#第六个图形是gamma分布(gamma distribution), 要求参数alpha 和beta都大于零。
plt.subplot(5,2,6)
plt.xlabel("random.gammavariate")
alpha = 1
beta = 10
res_6 = [random.gammavariate(alpha, beta) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_6, buckets)
#第七个图形是对数正态分布(Log normal distribution)。如果取这个分布的自然对数,会得到一个中值为mu,标准差为sigma的正态分布。mu可以取任何值,sigma必须大于零。
plt.subplot(5,2,7)
plt.xlabel("random.lognormalvariate")
mu = 1
sigma = 0.5
res_7 = [random.lognormvariate(mu, sigma) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_7, buckets)
#第八个图形是正态分布(normal distribution)。
plt.subplot(5,2,8)
plt.xlabel("random.normalvariate")
mu = 1
sigma = 0.5
res_8 = [random.normalvariate(mu, sigma) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_8, buckets)
#最后一个图形是帕累托分布(Pareto distribution), alpha 是形状参数。
plt.subplot(5,2,9)
plt.xlabel("random.normalvariate")
alpha = 1
res_9 = [random.paretovariate(alpha) for _ in xrange(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)]
plt.hist(res_9, buckets)
plt.show()
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。



