PyQt5主窗口动态加载Widget实例代码
本文研究的主要是PyQt5主窗口动态加载Widget的代码示例,具体如下。
我们通过Qt Designer设计两个窗口,命名为主窗口(MainForm)和子窗口(ChildrenForm)。我们在主窗口的空白中央添加一个栅格布局并命名为MaingridLayout,等会需要将ChildrenForm放进去。
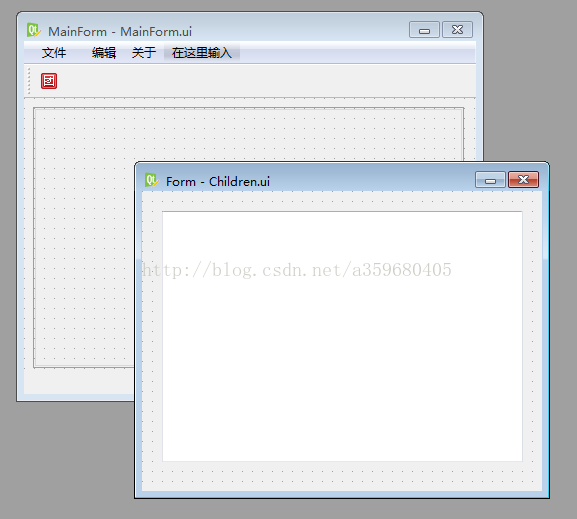
编写代码
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from MainForm import Ui_MainForm
from Children import Ui_Form
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QFileDialog
class MainForm(QtWidgets.QMainWindow,Ui_MainForm):
def __init__(self):
super(MainForm,self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self)
self.child=ChildrenForm() #self.child = children()生成子窗口实例self.child
self.fileOpen.triggered.connect(self.openMsg) #菜单的点击事件是triggered
self.fileClose.triggered.connect(self.close)
self.actionTst.triggered.connect(self.childShow) #点击actionTst,子窗口就会显示在主窗口的MaingridLayout中
def childShow(self):
self.MaingridLayout.addWidget(self.child) #添加子窗口
self.child.show()
def openMsg(self):
file,ok=QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self,"打开","C:/","All Files (*);;Text Files (*.txt)")
self.statusbar.showMessage(file) #在状态栏显示文件地址
class ChildrenForm(QtWidgets.QWidget,Ui_Form):
def __init__(self):
super(ChildrenForm,self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self)
if __name__=="__main__":
import sys
app=QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
myshow=MainForm()
myshow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
总结
以上就是本文关于PyQt5主窗口动态加载Widget实例代码的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站其他相关专题,如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!