Python实现数据结构线性链表(单链表)算法示例
本文实例讲述了Python实现数据结构线性链表(单链表)算法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
初学python,拿数据结构中的线性链表存储结构练练手,理论比较简单,直接上代码。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: Hui
# Date: 2017-10-13
# 结点类,
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # 数据域
self.next = None # 指针域
def get_data(self):
return self.data
# 链表类
class List:
def __init__(self, head):
self.head = head # 默认初始化头结点
def is_empty(self): # 空链表判断
return self.get_len() == 0
def get_len(self): # 返回链表长度
length = 0
temp = self.head
while temp is not None:
length += 1
temp = temp.next
return length
def append(self, node): # 追加结点(链表尾部追加)
temp = self.head
while temp.next is not None:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = node
def delete(self, index): # 删除结点
if index < 1 or index > self.get_len():
print "给定位置不合理"
return
if index == 1:
self.head = self.head.next
return
temp = self.head
cur_pos = 0
while temp is not None:
cur_pos += 1
if cur_pos == index-1:
temp.next = temp.next.next
temp = temp.next
def insert(self, pos, node): # 插入结点
if pos < 1 or pos > self.get_len():
print "插入结点位置不合理..."
return
temp = self.head
cur_pos = 0
while temp is not Node:
cur_pos += 1
if cur_pos == pos-1:
node.next = temp.next
temp.next =node
break
temp = temp.next
def reverse(self, head): # 反转链表
if head is None and head.next is None:
return head
pre = head
cur = head.next
while cur is not None:
temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
head.next = None
return pre
def print_list(self, head): # 打印链表
init_data = []
while head is not None:
init_data.append(head.get_data())
head = head.next
return init_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = Node("head")
list = List(head)
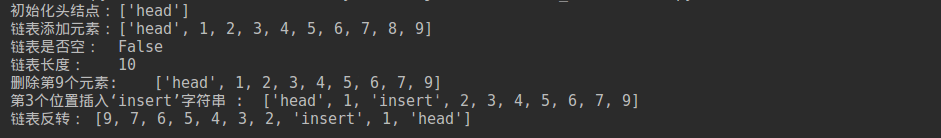
print '初始化头结点:\t', list.print_list(head)
for i in range(1, 10):
node = Node(i)
list.append(node)
print '链表添加元素:\t', list.print_list(head)
print '链表是否空:\t', list.is_empty()
print '链表长度:\t', list.get_len()
list.delete(9)
print '删除第9个元素:\t',list.print_list(head)
node = Node("insert")
list.insert(3, node)
print '第3个位置插入‘insert'字符串 :\t', list.print_list(head)
head = list.reverse(head)
print '链表反转:', list.print_list(head)
执行结果:
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python加密解密算法与技巧总结》、《Python编码操作技巧总结》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》及《Python入门与进阶经典教程》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。