关于初始种子自动选取的区域生长实例(python+opencv)
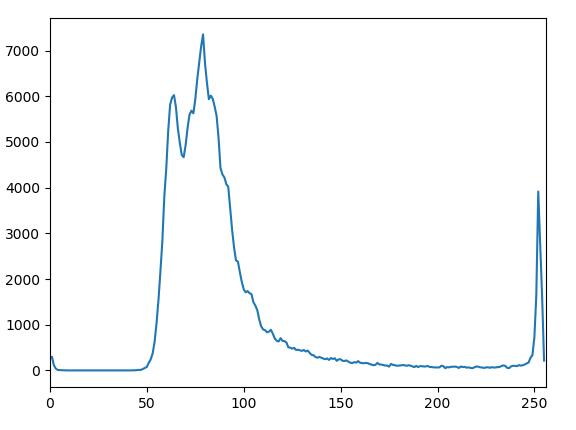
算法中,初始种子可自动选择(通过不同的划分可以得到不同的种子,可按照自己需要改进算法),图分别为原图(自己画了两笔为了分割成不同区域)、灰度图直方图、初始种子图、区域生长结果图。
另外,不管时初始种子选择还是区域生长,阈值选择很重要。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#初始种子选择
def originalSeed(gray, th):
ret, thresh = cv2.cv2.threshold(gray, th, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)#二值图,种子区域(不同划分可获得不同种子)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3,3))#3×3结构元
thresh_copy = thresh.copy() #复制thresh_A到thresh_copy
thresh_B = np.zeros(gray.shape, np.uint8) #thresh_B大小与A相同,像素值为0
seeds = [ ] #为了记录种子坐标
#循环,直到thresh_copy中的像素值全部为0
while thresh_copy.any():
Xa_copy, Ya_copy = np.where(thresh_copy > 0) #thresh_A_copy中值为255的像素的坐标
thresh_B[Xa_copy[0], Ya_copy[0]] = 255 #选取第一个点,并将thresh_B中对应像素值改为255
#连通分量算法,先对thresh_B进行膨胀,再和thresh执行and操作(取交集)
for i in range(200):
dilation_B = cv2.dilate(thresh_B, kernel, iterations=1)
thresh_B = cv2.bitwise_and(thresh, dilation_B)
#取thresh_B值为255的像素坐标,并将thresh_copy中对应坐标像素值变为0
Xb, Yb = np.where(thresh_B > 0)
thresh_copy[Xb, Yb] = 0
#循环,在thresh_B中只有一个像素点时停止
while str(thresh_B.tolist()).count("255") > 1:
thresh_B = cv2.erode(thresh_B, kernel, iterations=1) #腐蚀操作
X_seed, Y_seed = np.where(thresh_B > 0) #取处种子坐标
if X_seed.size > 0 and Y_seed.size > 0:
seeds.append((X_seed[0], Y_seed[0]))#将种子坐标写入seeds
thresh_B[Xb, Yb] = 0 #将thresh_B像素值置零
return seeds
#区域生长
def regionGrow(gray, seeds, thresh, p):
seedMark = np.zeros(gray.shape)
#八邻域
if p == 8:
connection = [(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 1), (1, 1), (1, 0), (1, -1), (0, -1)]
elif p == 4:
connection = [(-1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1)]
#seeds内无元素时候生长停止
while len(seeds) != 0:
#栈顶元素出栈
pt = seeds.pop(0)
for i in range(p):
tmpX = pt[0] + connection[i][0]
tmpY = pt[1] + connection[i][1]
#检测边界点
if tmpX < 0 or tmpY < 0 or tmpX >= gray.shape[0] or tmpY >= gray.shape[1]:
continue
if abs(int(gray[tmpX, tmpY]) - int(gray[pt])) < thresh and seedMark[tmpX, tmpY] == 0:
seedMark[tmpX, tmpY] = 255
seeds.append((tmpX, tmpY))
return seedMark
path = "_rg.jpg"
img = cv2.imread(path)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#hist = cv2.calcHist([gray], [0], None, [256], [0,256])#直方图
seeds = originalSeed(gray, th=253)
seedMark = regionGrow(gray, seeds, thresh=3, p=8)
#plt.plot(hist)
#plt.xlim([0, 256])
#plt.show()
cv2.imshow("seedMark", seedMark)
cv2.waitKey(0)
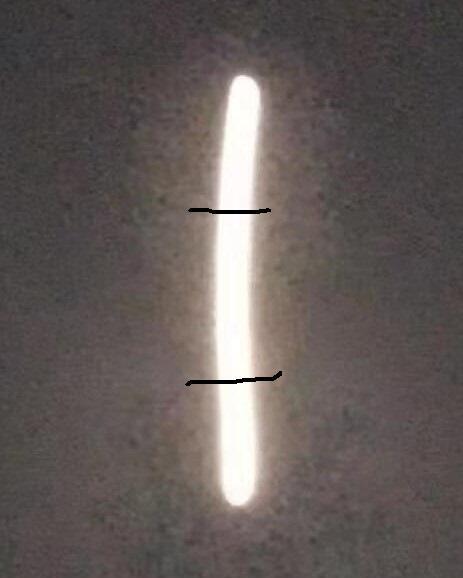


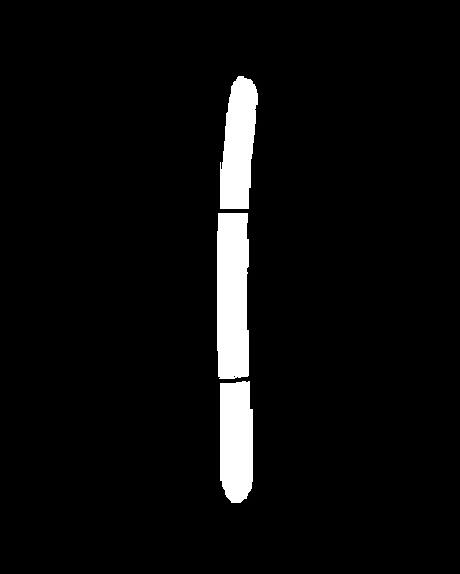
以上这篇关于初始种子自动选取的区域生长实例(python+opencv)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。