Python多线程同步---文件读写控制方法
1、实现文件读写的文件ltz_schedule_times.py
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding=utf-8
import os
def ReadTimes():
res = []
if os.path.exists('schedule_times.txt'):
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'r')
else:
os.system('touch schedule_times.txt')
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'r')
try:
line = fp.read()
if line == None or len(line)==0:
fp.close()
return 0
tmp = line.split()
print 'tmp: ', tmp
schedule_times = int(tmp[-1])
finally:
fp.close()
#print schedule_times
return schedule_times
def WriteTimes(schedule_times):
if schedule_times <= 10:
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'a+')#10以内追加进去
else:
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'w')#10以外重新写入
schedule_times = 1
print 'write schedule_times start!'
try:
fp.write(str(schedule_times)+'\n')
finally:
fp.close()
print 'write schedule_times finish!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
schedule_times = ReadTimes()
#if schedule_times > 10:
# schedule_times = 0
print schedule_times
schedule_times = schedule_times + 1
WriteTimes(schedule_times)
2.1、不加锁对文件进行多线程读写。
file_lock.py
#! /usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 from threading import Thread import threading import time from ltz_schedule_times import * #1、不加锁 def lock_test(): time.sleep(0.1) schedule_times = ReadTimes() print schedule_times schedule_times = schedule_times + 1 WriteTimes(schedule_times) if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): Thread(target = lock_test, args=()).start()
得到结果:
0 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: tmp: tmp: tmp: [[[['1''1''1''1']]]] 11 1 1 write schedule_times start!write schedule_times start! write schedule_times start!write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! write schedule_times finish! write schedule_times finish!write schedule_times finish!
文件写入结果:
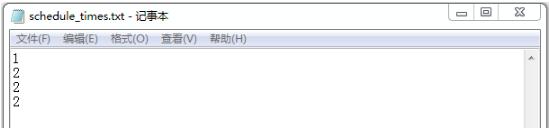
以上结果可以看出,不加锁多线程读写文件会出现错误。
2.2、加锁对文件进行多线程读写。
file_lock.py
#! /usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 from threading import Thread import threading import time from ltz_schedule_times import * #2、加锁 mu = threading.Lock() #1、创建一个锁 def lock_test(): #time.sleep(0.1) if mu.acquire(True): #2、获取锁状态,一个线程有锁时,别的线程只能在外面等着 schedule_times = ReadTimes() print schedule_times schedule_times = schedule_times + 1 WriteTimes(schedule_times) mu.release() #3、释放锁 if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): Thread(target = lock_test, args=()).start()
结果:
0 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1'] 1 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2'] 2 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2', '3'] 3 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2', '3', '4'] 4 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish!
文件写入结果:
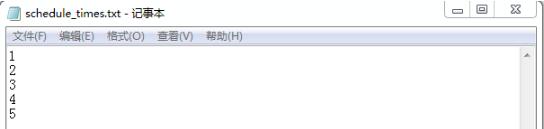
以上这篇Python多线程同步---文件读写控制方法就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。

