python算法题 链表反转详解
链表的反转是一个很常见、很基础的数据结构题,输入一个单向链表,输出逆序反转后的链表,如图:上面的链表转换成下面的链表。实现链表反转有两种方式,一种是循环迭代,另外一种方式是递归。
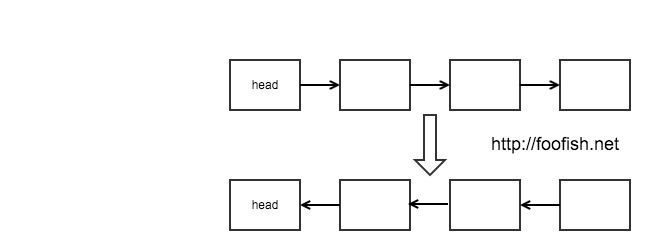
第一种方式:循坏迭代
循坏迭代算法需要三个临时变量:pre、head、next,临界条件是链表为None或者链表就只有一个节点。
# encoding: utf-8 class Node(object): def __init__(self): self.value = None self.next = None def __str__(self): return str(self.value) def reverse_loop(head): if not head or not head.next: return head pre = None while head: next = head.next # 缓存当前节点的向后指针,待下次迭代用 head.next = pre # 这一步是反转的关键,相当于把当前的向前指针作为当前节点的向后指针 pre = head # 作为下次迭代时的(当前节点的)向前指针 head = next # 作为下次迭代时的(当前)节点 return pre # 返回头指针,头指针就是迭代到最后一次时的head变量(赋值给了pre)
测试一下:
if __name__ == '__main__': three = Node() three.value = 3 two = Node() two.value = 2 two.next = three one = Node() one.value = 1 one.next = two head = Node() head.value = 0 head.next = one newhead = reverse_loop(head) while newhead: print(newhead.value, ) newhead = newhead.next
输出:
3 2 1 0 2
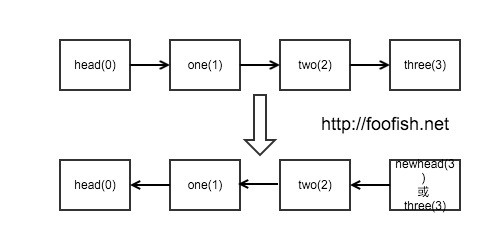
第二种方式:递归
递归的思想就是:
head.next = None head.next.next = head.next head.next.next.next = head.next.next ... ...
head的向后指针的向后指针转换成head的向后指针,依此类推。
实现的关键步骤就是找到临界点,何时退出递归。当head.next为None时,说明已经是最后一个节点了,此时不再递归调用。
def reverse_recursion(head): if not head or not head.next: return head new_head = reverse_recursion(head.next) head.next.next = head head.next = None return new_head
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。


