详解Python time库的使用
一、时间获取函数
>>> import time >>> time.time() 1570530861.740123 >>> time.ctime() 'Tue Oct 8 18:34:27 2019' >>> time.gmtime() time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=10, tm_min=34, tm_sec=52, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=281, tm_isdst=0)
二、时间格式化
time.strftime(format[, t])
format – 格式字符串。
t – 可选的参数t是一个struct_time对象。
python中时间日期格式化符号:
%Y 年份
%m 月份
%B 月份名称 January
%b 月份名称缩写 Jan
%d 日期
%A 星期 Monday
%a 星期缩写 Mon
%H 小时 24
%h 小时 12
%p 上下午
%M 分钟
%S 秒
>>> t=time.gmtime()
>>> time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", t)
'2019-10-08 10:38:06'
>>> time.strftime("%Y-%B-%d-%A-%H-%p-%S")
'2019-October-08-Tuesday-18-PM-50'
>>> time.strftime("%A-%p")
'Tuesday-PM'
>>> time.strftime("%M:%S")
'39:59'
三、时间进度条
测量时间:perf_counter() 返回系统运行时间。由于返回值的基准点是未定义的,所以,只有连续调用的结果之间的差才是有效的。
>>> start = time.perf_counter() >>> start 684.980333384 >>> end = time.perf_counter() >>> end 696.094559111 >>> end-start 11.114225726999962
产生时间:sleep(secs) 推迟调用线程的运行
secs:休眠时间;可以是浮点数,如time.sleep(2.7)
#TextProBarV3.py
import time
scale = 40
print('执行开始'.center(scale//2,'-'))
start = time.perf_counter()
for i in range(scale+1):
a = '*' * i
b = '.' * (scale - i)
c = (i / scale) * 100
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
print("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]{:.2f}".format(c,a,b,dur),end='')
time.sleep(0.1)
print('\n'+'执行结果'.center(scale//2,'-'))
四、七段数码管
七段数码管(seven-segment indicator)由7 段数码管拼接而成,每段有亮或不亮两种情况,改进型的七段数码管还包括一个小数点位置。
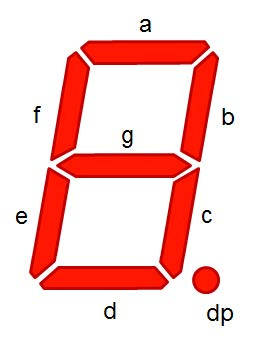
七段数码管能形成27=128 种不同状态,其中部分状态能够显示易于人们理解的数字或字母含义,因此被广泛使用。
#DrawSevenSegDisplay.py
import turtle, datetime
def drawGap(): #绘制数码管间隔
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(5)
def drawLine(draw): #绘制单段数码管
drawGap()
turtle.pendown() if draw else turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(40)
drawGap()
turtle.right(90)
def drawDigit(d): #根据数字绘制七段数码管
drawLine(True) if d in [2,3,4,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,3,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,6,8] else drawLine(False)
turtle.left(90)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,4,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,3,5,6,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,1,2,3,4,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
turtle.left(180)
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(20)
def drawDate(date):
turtle.pencolor("red")
for i in date:
if i == '-':
turtle.write('年',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
turtle.pencolor("green")
turtle.fd(40)
elif i == '=':
turtle.write('月',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
turtle.pencolor("blue")
turtle.fd(40)
elif i == '+':
turtle.write('日',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
else:
drawDigit(eval(i))
def main():
turtle.setup(800, 350, 200, 200)
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(-350)
turtle.pensize(5)
drawDate(datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m=%d+'))
turtle.hideturtle()
main()
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Python time库的使用,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对【听图阁-专注于Python设计】网站的支持!
如果你觉得本文对你有帮助,欢迎转载,烦请注明出处,谢谢!

