python多线程操作实例
一、python多线程
因为CPython的实现使用了Global Interpereter Lock(GIL),使得python中同一时刻只有一个线程在执行,从而简化了python解释器的实现,且python对象模型天然地线程安全。如果你想你的应用程序在多核的机器上使用更好的资源,建议使用multiprocessing或concurrent.futures.processpoolexecutor。但是如果你的程序是IO密集型,则使用线程仍然是很好的选择。
二、python多线程使用的两种方法
实例:
import threading
import time
def worker(num):
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' start')
time.sleep(10)
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' running')
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + " " + str(num))
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' exit')
def deamon():
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' start')
time.sleep(20)
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' running')
print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' exit')
print(threading.currentThread().getName())
d = threading.Thread(name='deamon', target=deamon)
d.setDaemon(True)
d.start()
w = threading.Thread(name='worker', target=worker, args=(10,))
w.start()
class myWorker(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, num):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.num = num
self.thread_stop = False
def run(self):
print (self.getName()+' start')
time.sleep(30)
print (self.getName()+' running')
print (self.getName()+" " + str(self.num))
print (self.getName()+' exit')
mw = myWorker(30)
mw.setName("MyWorker")
mw.start()
print(threading.currentThread().getName())
print("All threads:")
print("------------")
for th in threading.enumerate():
print(th.getName())
print("------------")
d.join()
w.join()
mw.join()
print(threading.currentThread().getName())
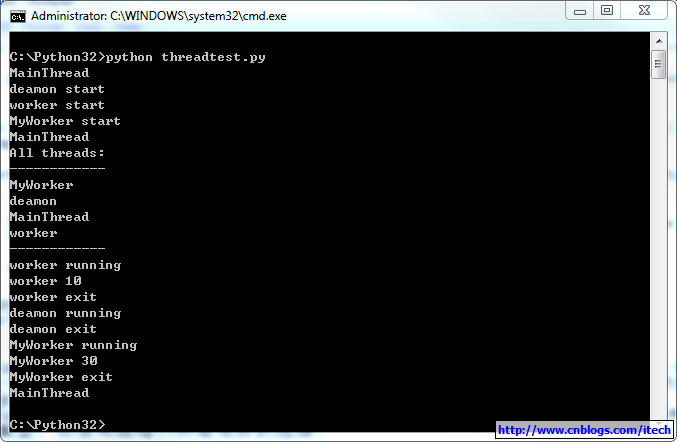
运行结果如下:
1)python线程使用的两种方法:
**直接调用threading.Thread来构造thread对象,Thread的参数如下:
class threading.Thread(group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(), kwargs={})
group为None;
target为线程将要执行的功能函数;
name为线程的名字,也可以在对象构造后调用setName()来设定;
args为tuple类型的参数,可以为多个,如果只有一个也的使用tuple的形式传入,例如(1,);
kwargs为dict类型的参数,也即位命名参数;
**实现自己的threading.Thread的子类,需要重载__init__()和run()。
2)threading.Thread对象的其他方法:
start(),用来启动线程;
join(), 等待直到线程结束;
setDeamon(), 设置线程为deamon线程,必须在start()调用前调用,默认为非demon。
注意: python的主线程在没有非deamon线程存在时就会退出。
3)threading的静态方法:
threading.current_thread() , 用来获得当前的线程;
threading.enumerate() , 用来多的当前存活的所有线程;
threading.Timer 定时器,其实是thread的一个字类型,使用如下:
def hello(): print("hello, world")
t = Timer(30.0, hello)
t.start()
4)logging是线程安全的
logging 模块是线程安全的,所以可以使用logging来帮助调试多线程程序。
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format="(%(threadName)-10s : %(message)s",
)
logging.debug("wait_for_event_timeout starting")