Python 爬虫学习笔记之单线程爬虫
介绍
本篇文章主要介绍如何爬取麦子学院的课程信息(本爬虫仍是单线程爬虫),在开始介绍之前,先来看看结果示意图
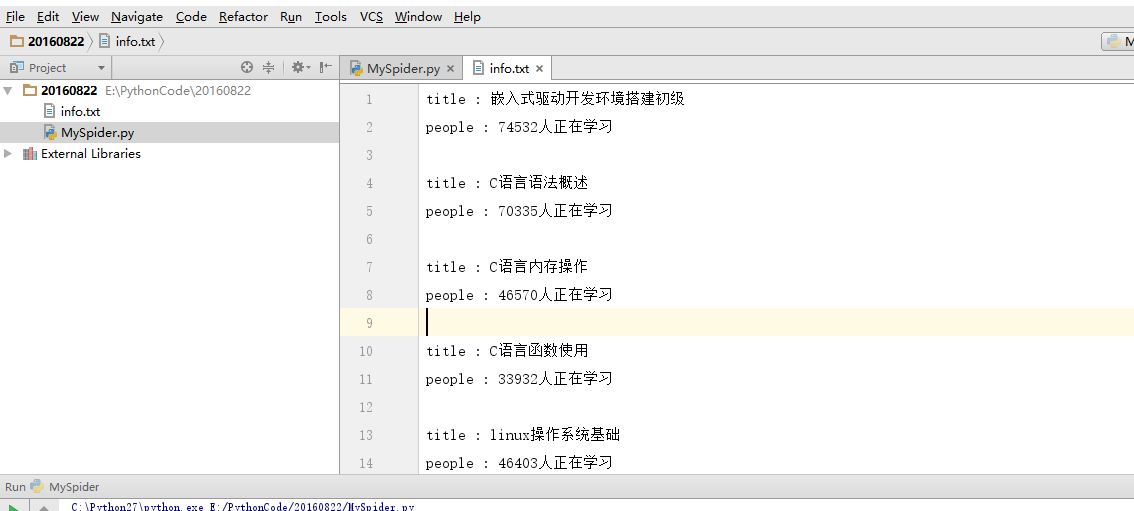
怎么样,是不是已经跃跃欲试了?首先让我们打开麦子学院的网址,然后找到麦子学院的全部课程信息,像下面这样

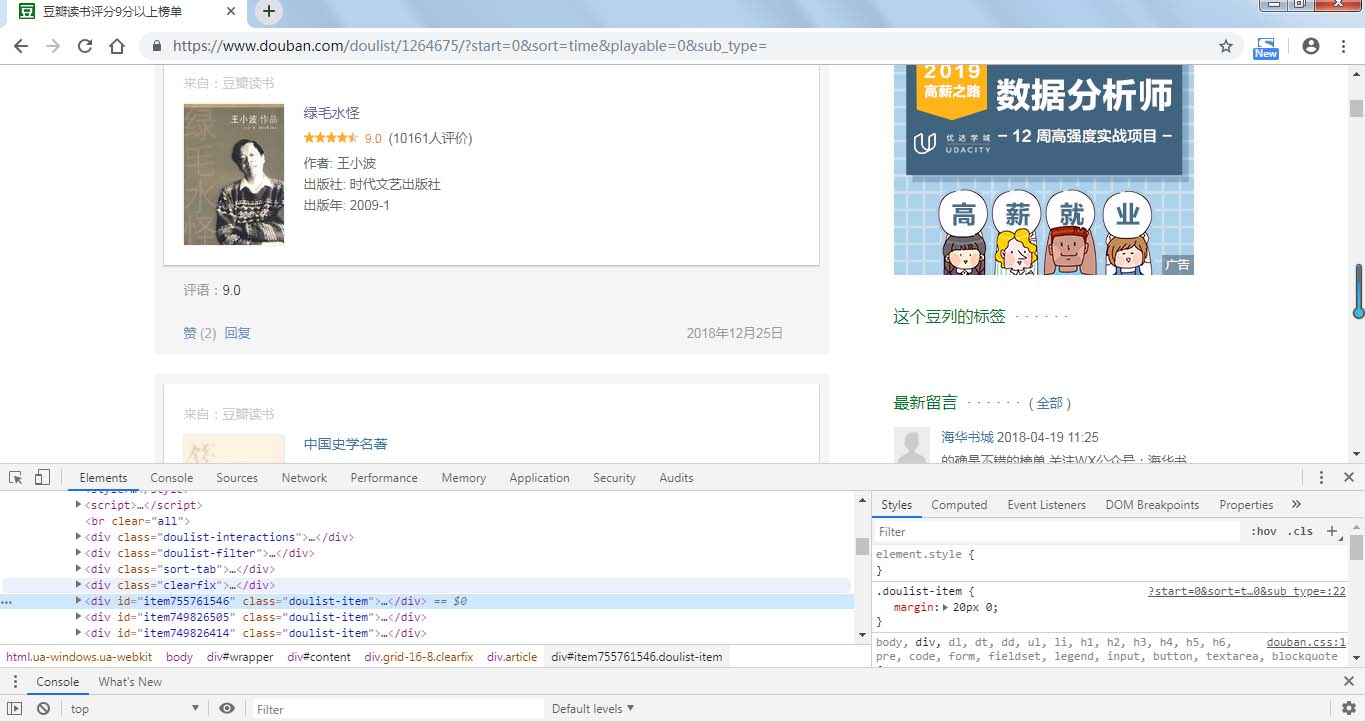
这个时候进行翻页,观看网址的变化,首先,第一页的网址是 http://www.maiziedu.com/course/list/, 第二页变成了 http://www.maiziedu.com/course/list/all-all/0-2/, 第三页变成了 http://www.maiziedu.com/course/list/all-all/0-3/ ,可以看到,每次翻一页,0后面的数字就会递增1,然后就有人会想到了,拿第一页呢?我们尝试着将 http://www.maiziedu.com/course/list/all-all/0-1/ 放进浏览器的地址栏,发现可以打开第一栏,那就好办了,我们只需要使用 re.sub() 就可以很轻松的获取到任何一页的内容。获取到网址链接之后,下面要做的就是获取网页的源代码,首先右击查看审查或者是检查元素,就可以看到以下界面
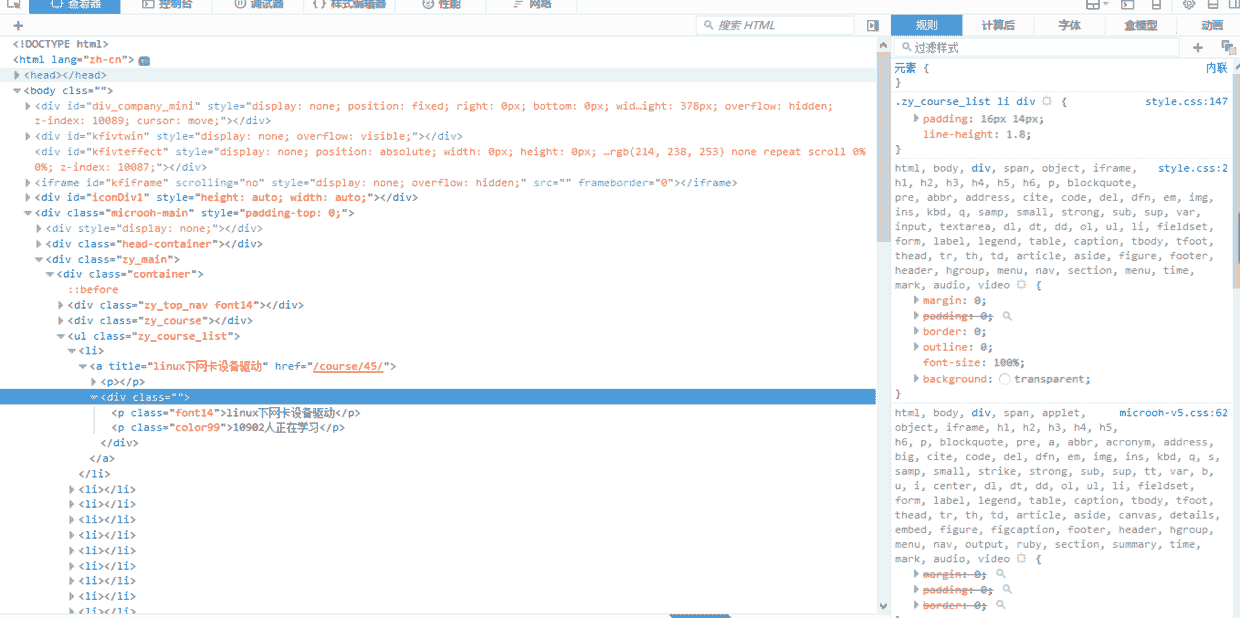
找到课程所在的位置以后,就可以很轻松的利用正则表达式将我们需要的内容提取出来,至于怎么提取,那就要靠你自己了,尝试着自己去找规律才能有更大的收获。如果你实在不知道怎么提取,那么继续往下,看我的源代码吧
实战源代码
# coding=utf-8
import re
import requests
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf8")
class spider():
def __init__(self):
print "开始爬取内容。。。"
def changePage(self, url, total_page):
nowpage = int(re.search('/0-(\d+)/', url, re.S).group(1))
pagegroup = []
for i in range(nowpage, total_page + 1):
link = re.sub('/0-(\d+)/', '/0-%s/' % i, url, re.S)
pagegroup.append(link)
return pagegroup
def getsource(self, url):
html = requests.get(url)
return html.text
def getclasses(self, source):
classes = re.search('<ul class="zy_course_list">(.*?)</ul>', source, re.S).group(1)
return classes
def geteach(self, classes):
eachclasses = re.findall('<li>(.*?)</li>', classes, re.S)
return eachclasses
def getinfo(self, eachclass):
info = {}
info['title'] = re.search('<a title="(.*?)"', eachclass, re.S).group(1)
info['people'] = re.search('<p class="color99">(.*?)</p>', eachclass, re.S).group(1)
return info
def saveinfo(self, classinfo):
f = open('info.txt', 'a')
for each in classinfo:
f.writelines('title : ' + each['title'] + '\n')
f.writelines('people : ' + each['people'] + '\n\n')
f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
classinfo = []
url = 'http://www.maiziedu.com/course/list/all-all/0-1/'
maizispider = spider()
all_links = maizispider.changePage(url, 30)
for each in all_links:
htmlsources = maizispider.getsource(each)
classes = maizispider.getclasses(htmlsources)
eachclasses = maizispider.geteach(classes)
for each in eachclasses:
info = maizispider.getinfo(each)
classinfo.append(info)
maizispider.saveinfo(classinfo)
以上代码并不难懂,基本就是正则表达式的使用,然后直接运行就可以看到开头我们的截图内容了,由于这是单线程爬虫,所以运行速度感觉有点慢,接下来还会继续更新多线程爬虫。
应小伙伴们的要求,下面附上requests爬虫库的安装和简单示例
首先安装pip包管理工具,下载get-pip.py. 我的机器上安装的既有python2也有python3。
安装pip到python2:
python get-pip.py
安装到python3:
python3 get-pip.py
pip安装完成以后,安装requests库开启python爬虫学习。
安装requests
pip3 install requests
我使用的python3,python2可以直接用pip install requests.
入门例子
import requests
html=requests.get("http://gupowang.baijia.baidu.com/article/283878")
html.encoding='utf-8'
print(html.text)
第一行引入requests库,第二行使用requests的get方法获取网页源代码,第三行设置编码格式,第四行文本输出。
把获取到的网页源代码保存到文本文件中:
import requests
import os
html=requests.get("http://gupowang.baijia.baidu.com/article/283878")
html_file=open("news.txt","w")
html.encoding='utf-8'
print(html.text,file=html_file)