python实现的多线程端口扫描功能示例
本文实例讲述了python实现的多线程端口扫描功能。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
下面的程序给出了对给定的ip主机进行多线程扫描的Python代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
#encoding: utf-8
import socket, sys, thread, time
openPortNum = 0
socket.setdefaulttimeout(3)
def usage():
print '''''Usage:
Scan the port of one IP: python port_scan_multithread.py -o <ip>
Scan the port of one IP: python port_scan_multithread.py -m <ip1, ip2, ip3, ip4 ...>
'''
print 'Exit'
sys.exit(1)
def socket_port(ip, PORT):
global openPortNum
if PORT > 65535:
print 'Port scanning beyond the port range, interrupt to scan'
sys.exit(1)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
result = s.connect_ex((ip, PORT))
if(result == 0):
print ip, PORT,'is open'
openPortNum += 1
s.close()
def start_scan(IP):
for port in range(0, 65535+1):
thread.start_new_thread(socket_port, (IP, int(port)))
time.sleep(0.006)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = 0
if len(sys.argv)<2 or sys.argv[1] == '-h':
usage()
elif sys.argv[1] == '-o':
ONE_IP = raw_input('Please input ip of scanning: ')
t = time.time()
start_scan(ONE_IP)
elif sys.argv[1] == '-m':
MANY_IP = raw_input('Please input many ip of scanning: ')
IP_SEG = MANY_IP.split(',')
t = time.time()
for i in IP_SEG:
start_scan(i)
print
print 'total open port is %s, scan used time is: %f ' % (openPortNum, time.time()-t)
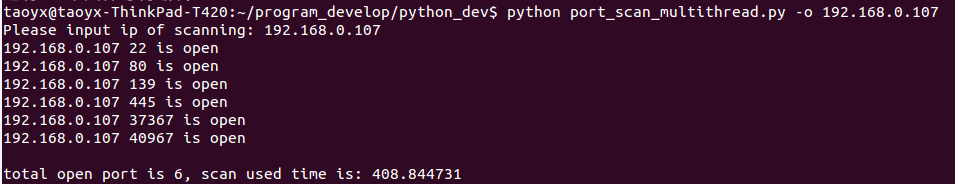
运行效果图
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python URL操作技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python Socket编程技巧总结》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。