Python实现Linux的find命令实例分享
使用Python实现简单Linux的find命令
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
#*-*coding:utf8*-*
from optparse import OptionParser
import os
import sys
#使用选项帮助信息可以使用中文
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")
#定义选项以及命令使用帮助信息
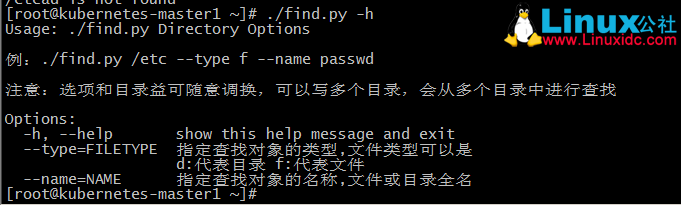
usage = sys.argv[0] + " Directory Options\n\n例:"+sys.argv[0] + " /etc --type f --name passwd\n\n注意:选项和目录益可随意调换,可以写多个目录,会从多个目录中进行查找"
parser = OptionParser(usage)
parser.add_option("--type",
dest="filetype",
action="store",
default=False,
help="指定查找对象的类型,文件类型可以是 d:代表目录 f:代表文件")
parser.add_option("--name",
dest="name",
action="store",
default=False,
help="指定查找对象的名称,文件或目录全名")
options, args = parser.parse_args()
def find(dir):
directory = os.walk(dir)
for x, y, z in directory:
if options.filetype == "f":
for name in z:
if name == options.name:
path = os.path.join(x,name)
print(path)
if options.filetype == "d":
for name in y:
if name == options.name:
path = os.path.join(x,name)
print(path)
#判断目录是否存在,并且是否为目录
for dir in args:
if os.path.exists(dir) == False:
sys.stderr.write(dir+" is not found\n")
exit(100)
if os.path.isfile(dir):
sys.stderr.write(dir+" is a file\n")
exit(101)
#判断--type选项是否正确,只能跟 f 或者 d
if not (options.filetype == "f" or options.filetype == "d"):
sys.stderr.write("--type only support d or f\n")
exit(102)
if __name__ == "__main__":
for dir in args:
find(dir)
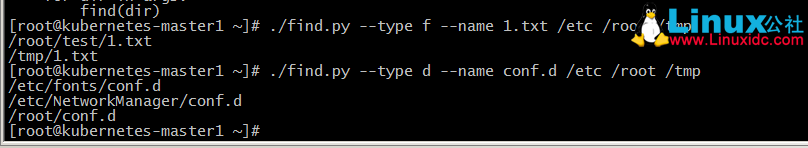
运行结果如下: