机器学习经典算法-logistic回归代码详解
一、算法简要
我们希望有这么一种函数:接受输入然后预测出类别,这样用于分类。这里,用到了数学中的sigmoid函数,sigmoid函数的具体表达式和函数图象如下:
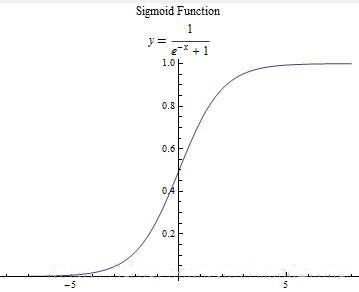
可以较为清楚的看到,当输入的x小于0时,函数值<0.5,将分类预测为0;当输入的x大于0时,函数值>0.5,将分类预测为1。
1.1 预测函数的表示
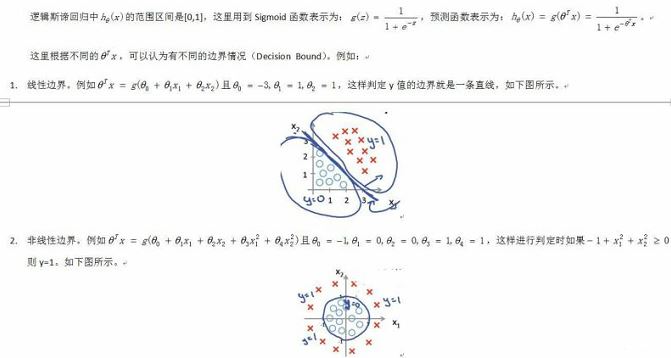
1.2参数的求解

二、代码实现
函数sigmoid计算相应的函数值;gradAscent实现的batch-梯度上升,意思就是在每次迭代中所有数据集都考虑到了;而stoGradAscent0中,则是将数据集中的示例都比那里了一遍,复杂度大大降低;stoGradAscent1则是对随机梯度上升的改进,具体变化是alpha每次变化的频率是变化的,而且每次更新参数用到的示例都是随机选取的。
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def loadDataSet():
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
fr = open('testSet.txt')
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip('\n').split('\t')
dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2]))
fr.close()
return dataMat, labelMat
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX))
def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn)
labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose()
m,n=shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.001
maxCycles = 500
weights = ones((n,1))
errors=[]
for k in range(maxCycles):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)
error = labelMat - h
errors.append(sum(error))
weights = weights + alpha*dataMatrix.transpose()*error
return weights, errors
def stoGradAscent0(dataMatIn, classLabels):
m,n=shape(dataMatIn)
alpha = 0.01
weights = ones(n)
for i in range(m):
h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatIn[i]*weights))
error = classLabels[i] - h
weights = weights + alpha*error*dataMatIn[i]
return weights
def stoGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter = 150):
m,n=shape(dataMatrix)
weights = ones(n)
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex=range(m)
for i in range(m):
alpha= 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.01
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))
h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights))
error = classLabels[randIndex]-h
weights=weights+alpha*error*dataMatrix[randIndex]
del(dataIndex[randIndex])
return weights
def plotError(errs):
k = len(errs)
x = range(1,k+1)
plt.plot(x,errs,'g--')
plt.show()
def plotBestFit(wei):
weights = wei.getA()
dataMat, labelMat = loadDataSet()
dataArr = array(dataMat)
n = shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1=[]
ycord1=[]
xcord2=[]
ycord2=[]
for i in range(n):
if int(labelMat[i])==1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green')
x = arange(-3.0,3.0,0.1)
y=(-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2]
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.show()
def classifyVector(inX, weights):
prob = sigmoid(sum(inX*weights))
if prob>0.5:
return 1.0
else:
return 0
def colicTest(ftr, fte, numIter):
frTrain = open(ftr)
frTest = open(fte)
trainingSet=[]
trainingLabels=[]
for line in frTrain.readlines():
currLine = line.strip('\n').split('\t')
lineArr=[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21]))
frTrain.close()
trainWeights = stoGradAscent1(array(trainingSet),trainingLabels, numIter)
errorCount = 0
numTestVec = 0.0
for line in frTest.readlines():
numTestVec += 1.0
currLine = line.strip('\n').split('\t')
lineArr=[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
if int(classifyVector(array(lineArr), trainWeights))!=int(currLine[21]):
errorCount += 1
frTest.close()
errorRate = (float(errorCount))/numTestVec
return errorRate
def multiTest(ftr, fte, numT, numIter):
errors=[]
for k in range(numT):
error = colicTest(ftr, fte, numIter)
errors.append(error)
print "There "+str(len(errors))+" test with "+str(numIter)+" interations in all!"
for i in range(numT):
print "The "+str(i+1)+"th"+" testError is:"+str(errors[i])
print "Average testError: ", float(sum(errors))/len(errors)
'''''
data, labels = loadDataSet()
weights0 = stoGradAscent0(array(data), labels)
weights,errors = gradAscent(data, labels)
weights1= stoGradAscent1(array(data), labels, 500)
print weights
plotBestFit(weights)
print weights0
weights00 = []
for w in weights0:
weights00.append([w])
plotBestFit(mat(weights00))
print weights1
weights11=[]
for w in weights1:
weights11.append([w])
plotBestFit(mat(weights11))
'''
multiTest(r"horseColicTraining.txt",r"horseColicTest.txt",10,500)
总结
以上就是本文关于机器学习经典算法-logistic回归代码详解的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站:
如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!