python通过elixir包操作mysql数据库实例代码
本文研究的主要是python通过elixir包操作mysql数据库的相关实例,具体如下。
python操作数据库有很多方法,下面介绍elixir来操作数据库。elixir是对sqlalchemy lib的一个封装,classes和tables是一一对应的,能够一步定义classes,tables和mappers,支持定义多个primary key。
定义model.py
from elixir import sqlalchemy
from elixir import *
engine =sqlalchemy.create_engine('mysql://root:root@localhost/') #the first root is the user, and the sencond root is the password
#engine.execute("DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS elixir")
engine.execute("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS elixir")
metadata.bind='mysql://root:root@localhost:3306/elixir'
#metadata.bind.echo =True
class Movie(Entity):
using_options(tablename='movies')
title = Field(Unicode(30),primary_key = True)
year = Field(Integer, primary_key = True)
description = Field(UnicodeText)
director = ManyToOne('Director')
genres = ManyToMany('Genre')
actor = ManyToMany('Actor')
def __repr__(self):
return '<Move "%s" (%d)>' % (self.title, self.year)
class Person(Entity):
using_options(inheritance='multi')
using_options(tablename='person')
name = Field(Unicode(60))
def __repr__(self):
return '<Person "%s">' % self.name
class Director(Person):
using_options(inheritance='multi')
using_options(tablename='director')
movies = OneToMany('Movie')
def __repr__(self):
return '<Director "%s">' % self.name
class Genre(Person):
using_options(inheritance='multi')
using_options(tablename='genre')
movies = ManyToMany('Movie')
def __repr__(self):
return '<Genre "%s">' % self.name
class Actor(Person):
using_options(inheritance='multi')
using_options(tablename='actor')
movies = ManyToMany('Movie')
def __repr__(self):
return '<Actor "%s">' % self.name
model_test.py
from model import * # setup_all(True) is equal to the following two staps: setup_all() # create sqlalchemy table object as mapper object for the class create_all() # take all table objcts and create real tables by issuing SQL statements on the databse. Actor1 = Actor(name=u"lvliang") scifi = Genre(name = u"Science-Fiction") rscott = Director(name = u"Ridley Scott") glucas = Director(name = u"George Lucas") alien = Movie(title = u"Alien", year = 1979, director=rscott, genres=[scifi, Genre(name=u"Horror")], actor = [Actor1]) brunner = Movie(title = u"Blade Runner", year = 1982, director = rscott, genres=[scifi]) swars = Movie(title = u"Star Wars", year = 1977, director = glucas, genres=[scifi]) session.commit() m1 = Movie.query.filter_by(title=u"Alien").one() m2 = Movie.query.filter(Movie.year>1980).all() m3 = Movie.query.filter(Movie.director.has(name = u"Ridley Scott")).all() m4 = Movie.query.filter(Movie.director.has(Director.name.endswith(u"Scott"))).all() m5 = Movie.query.filter(Movie.genres.any(name = u"Horror")).all() print m1 print m2 print m3 print m4 print m5 d = Director.get_by(name = u"Ridley Scott") # Class.get_by(xxx) is a shortcut for Class.query.filter_by(xxx).first q = Movie.query.filter_by(director = d) #get all movies directed by director d m = q.filter_by(year = 1979).all() print "Movie direct by %s in year 1979 are " %(d.name) print m movies = q.order_by(sqlalchemy.desc(Movie.year)).all() print movies fro m in movies: m.delete() session.commit()
执行model.py,结果为:
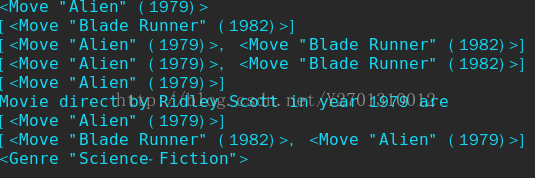
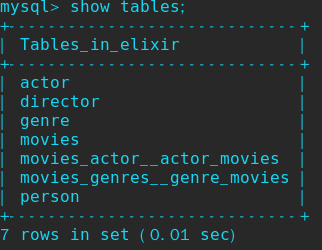
查看数据库,结果为:
总结
以上就是本文关于python通过elixir包操作mysql数据库实例代码的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站其他相关专题,如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!