Python实现k-means算法
本文实例为大家分享了Python实现k-means算法的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
这也是周志华《机器学习》的习题9.4。
数据集是西瓜数据集4.0,如下
编号,密度,含糖率
1,0.697,0.46
2,0.774,0.376
3,0.634,0.264
4,0.608,0.318
5,0.556,0.215
6,0.403,0.237
7,0.481,0.149
8,0.437,0.211
9,0.666,0.091
10,0.243,0.267
11,0.245,0.057
12,0.343,0.099
13,0.639,0.161
14,0.657,0.198
15,0.36,0.37
16,0.593,0.042
17,0.719,0.103
18,0.359,0.188
19,0.339,0.241
20,0.282,0.257
21,0.784,0.232
22,0.714,0.346
23,0.483,0.312
24,0.478,0.437
25,0.525,0.369
26,0.751,0.489
27,0.532,0.472
28,0.473,0.376
29,0.725,0.445
30,0.446,0.459
算法很简单,就不解释了,代码也不复杂,直接放上来:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Excercise 9.4"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import random
data = pd.read_csv(filepath_or_buffer = '../dataset/watermelon4.0.csv', sep = ',')[["密度","含糖率"]].values
########################################## K-means #######################################
k = int(sys.argv[1])
#Randomly choose k samples from data as mean vectors
mean_vectors = random.sample(data,k)
def dist(p1,p2):
return np.sqrt(sum((p1-p2)*(p1-p2)))
while True:
print mean_vectors
clusters = map ((lambda x:[x]), mean_vectors)
for sample in data:
distances = map((lambda m: dist(sample,m)), mean_vectors)
min_index = distances.index(min(distances))
clusters[min_index].append(sample)
new_mean_vectors = []
for c,v in zip(clusters,mean_vectors):
new_mean_vector = sum(c)/len(c)
#If the difference betweenthe new mean vector and the old mean vector is less than 0.0001
#then do not updata the mean vector
if all(np.divide((new_mean_vector-v),v) < np.array([0.0001,0.0001]) ):
new_mean_vectors.append(v)
else:
new_mean_vectors.append(new_mean_vector)
if np.array_equal(mean_vectors,new_mean_vectors):
break
else:
mean_vectors = new_mean_vectors
#Show the clustering result
total_colors = ['r','y','g','b','c','m','k']
colors = random.sample(total_colors,k)
for cluster,color in zip(clusters,colors):
density = map(lambda arr:arr[0],cluster)
sugar_content = map(lambda arr:arr[1],cluster)
plt.scatter(density,sugar_content,c = color)
plt.show()
运行方式:在命令行输入 python k_means.py 4。其中4就是k。
下面是k分别等于3,4,5的运行结果,因为一开始的均值向量是随机的,所以每次运行结果会有不同。
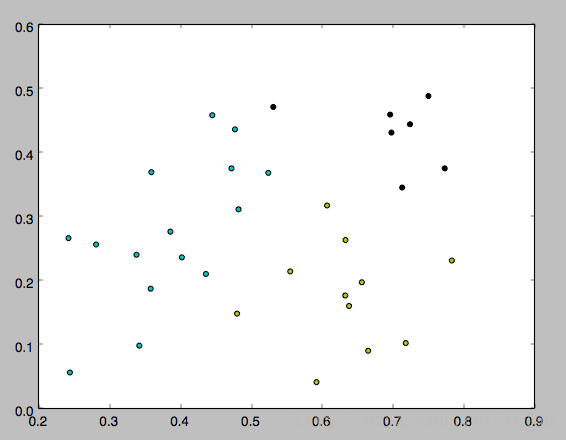
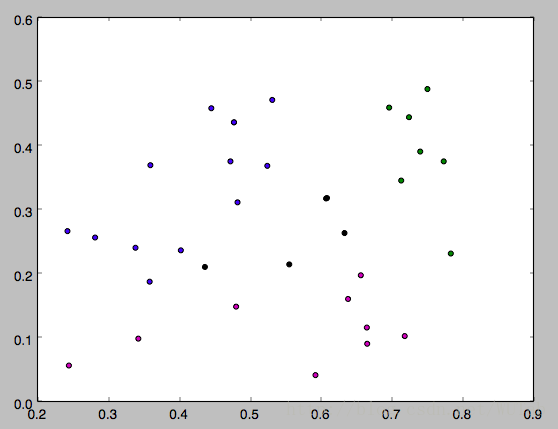
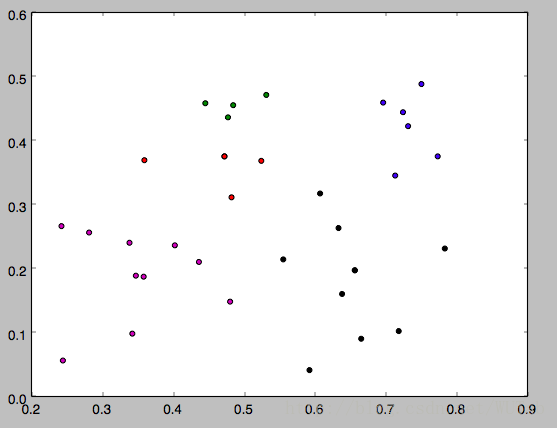
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。