遗传算法python版
本文实例为大家分享了python遗传算法的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
1、基本概念

遗传算法(GA)是最早由美国Holland教授提出的一种基于自然界的“适者生存,优胜劣汰”基本法则的智能搜索算法。该法则很好地诠释了生物进化的自然选择过程。遗传算法也是借鉴该基本法则,通过基于种群的思想,将问题的解通过编码的方式转化为种群中的个体,并让这些个体不断地通过选择、交叉和变异算子模拟生物的进化过程,然后利用“优胜劣汰”法则选择种群中适应性较强的个体构成子种群,然后让子种群重复类似的进化过程,直到找到问题的最优解或者到达一定的进化(运算)时间。
Ga算法中的几个重要名词概念。
个体(染色体):自然界中一个个体(染色体)代表一个生物,在GA算法中,个体(染色体)代表了具体问题的一个解。

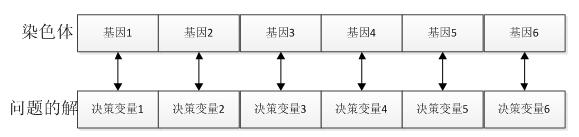
基因:在GA算法中,基因代表了具体问题解的一个决策变量,问题解和染色体中基因的对应关系如下所示:
种群:多个个体即组成一个种群。GA算法中,一个问题的多组解即构成了问题的解的种群。
2、主要步骤
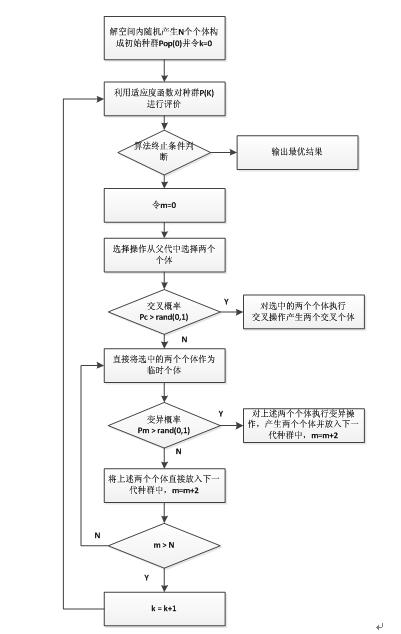
GA算法的基本步骤如下:
Step 1. 种群初始化。选择一种编码方案然后在解空间内通过随机生成的方式初始化一定数量的个体构成GA的种群。
Step 2. 评估种群。利用启发式算法对种群中的个体(矩形件的排入顺序)生成排样图并依此计算个体的适应函数值(利用率),然后保存当前种群中的最优个体作为搜索到的最优解。
Step 3. 选择操作。根据种群中个体的适应度的大小,通过轮盘赌或者期望值方法,将适应度高的个体从当前种群中选择出来。
Step 4. 交叉操作。将上一步骤选择的个体,用一定的概率阀值Pc控制是否利用单点交叉、多点交叉或者其他交叉方式生成新的交叉个体。
Step 5. 变异操作。用一定的概率阀值Pm控制是否对个体的部分基因执行单点变异或多点变异。
Step 6. 终止判断。若满足终止条件,则终止算法,否则返回Step 2。
流程图如下所示:
3、主要操作介绍
3.1 种群初始化
种群的初始化和具体的问题有关。比如一个问题有n个决策变量{x1,x2,…,xn}。每个决策变量有取值范围:下界{L1,L2,…,Ln}和上界{U1,U2,…,Un},则种群中个体的初始化即随机地在决策变量的取值范围内生成各个决策变量的值:Xj={x1,x2,...,xn},其中xi属于范围(Li,Ui)内。所有的个体即构成种群。当每个个体都初始化后,即种群完成初始化。
3.2 评价种群
种群的评价即计算种群中个体的适应度值。假设种群population有popsize个个体。依次计算每个个体的适应度值及评价种群。
3.3 选择操作
GA算法中常见的选择操作有轮盘赌方式:种群中适应度值更优的个体被选择的概率越大。假设popsize=4,按照如下表达式计算各个个体的被选择概率的大小,然后用圆饼图表示如下。
P(Xj) = fit(Xj)/(fit(X1)+fit(X2)+fit(X3)+fit(X4)),j=1,2,3,4
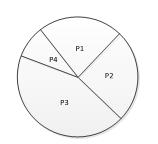
当依据轮盘赌方式进行选择时,则概率越大的越容易被选择到。
3.4 交叉操作
交叉操作也有许多种:单点交叉,两点交叉等。此处仅讲解一下两点交叉。首先利用选择操作从种群中选择两个父辈个体parent1和parent2,然后随机产生两个位置pos1和pos2,将这两个位置中间的基因位信息进行交换,便得到下图所示的off1和off2两个个体,但是这两个个体中一般会存在基因位信息冲突的现象(整数编码时),此时需要对off1和off2个体进行调整:off1中的冲突基因根据parent1中的基因调整为parent2中的相同位置处的基因。如off1中的“1”出现了两次,则第二处的“1”需要调整为parent1中“1”对应的parent2中的“4”,依次类推处理off1中的相冲突的基因。需要注意的是,调整off2,则需要参考parent2。

3.5 变异操作
变异操作的话,根据不同的编码方式有不同的变异操作。
如果是浮点数编码,则变异可以就染色体中间的某一个基因位的信息进行变异(重新生成或者其他调整方案)。
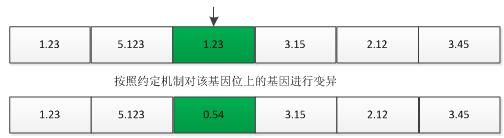
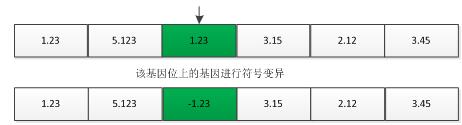
如果是采用整数编码方案,则一般有多种变异方法:位置变异和符号变异。
位置变异:

符号变异:
4、Python代码
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import random
import math
from operator import itemgetter
class Gene:
'''''
This is a class to represent individual(Gene) in GA algorithom
each object of this class have two attribute: data, size
'''
def __init__(self,**data):
self.__dict__.update(data)
self.size = len(data['data'])#length of gene
class GA:
'''''
This is a class of GA algorithm.
'''
def __init__(self,parameter):
'''''
Initialize the pop of GA algorithom and evaluate the pop by computing its' fitness value .
The data structure of pop is composed of several individuals which has the form like that:
{'Gene':a object of class Gene, 'fitness': 1.02(for example)}
Representation of Gene is a list: [b s0 u0 sita0 s1 u1 sita1 s2 u2 sita2]
'''
#parameter = [CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize, low, up]
self.parameter = parameter
low = self.parameter[4]
up = self.parameter[5]
self.bound = []
self.bound.append(low)
self.bound.append(up)
pop = []
for i in range(self.parameter[3]):
geneinfo = []
for pos in range(len(low)):
geneinfo.append(random.uniform(self.bound[0][pos], self.bound[1][pos]))#initialise popluation
fitness = evaluate(geneinfo)#evaluate each chromosome
pop.append({'Gene':Gene(data = geneinfo), 'fitness':fitness})#store the chromosome and its fitness
self.pop = pop
self.bestindividual = self.selectBest(self.pop)#store the best chromosome in the population
def selectBest(self, pop):
'''''
select the best individual from pop
'''
s_inds = sorted(pop, key = itemgetter("fitness"), reverse = False)
return s_inds[0]
def selection(self, individuals, k):
'''''
select two individuals from pop
'''
s_inds = sorted(individuals, key = itemgetter("fitness"), reverse=True)#sort the pop by the reference of 1/fitness
sum_fits = sum(1/ind['fitness'] for ind in individuals) #sum up the 1/fitness of the whole pop
chosen = []
for i in xrange(k):
u = random.random() * sum_fits#randomly produce a num in the range of [0, sum_fits]
sum_ = 0
for ind in s_inds:
sum_ += 1/ind['fitness']#sum up the 1/fitness
if sum_ > u:
#when the sum of 1/fitness is bigger than u, choose the one, which means u is in the range of [sum(1,2,...,n-1),sum(1,2,...,n)] and is time to choose the one ,namely n-th individual in the pop
chosen.append(ind)
break
return chosen
def crossoperate(self, offspring):
'''''
cross operation
'''
dim = len(offspring[0]['Gene'].data)
geninfo1 = offspring[0]['Gene'].data#Gene's data of first offspring chosen from the selected pop
geninfo2 = offspring[1]['Gene'].data#Gene's data of second offspring chosen from the selected pop
pos1 = random.randrange(1,dim)#select a position in the range from 0 to dim-1,
pos2 = random.randrange(1,dim)
newoff = Gene(data = [])#offspring produced by cross operation
temp = []
for i in range(dim):
if (i >= min(pos1,pos2) and i <= max(pos1,pos2)):
temp.append(geninfo2[i])
#the gene data of offspring produced by cross operation is from the second offspring in the range [min(pos1,pos2),max(pos1,pos2)]
else:
temp.append(geninfo1[i])
#the gene data of offspring produced by cross operation is from the frist offspring in the range [min(pos1,pos2),max(pos1,pos2)]
newoff.data = temp
return newoff
def mutation(self, crossoff, bound):
'''''
mutation operation
'''
dim = len(crossoff.data)
pos = random.randrange(1,dim)#chose a position in crossoff to perform mutation.
crossoff.data[pos] = random.uniform(bound[0][pos],bound[1][pos])
return crossoff
def GA_main(self):
'''''
main frame work of GA
'''
popsize = self.parameter[3]
print("Start of evolution")
# Begin the evolution
for g in range(NGEN):
print("-- Generation %i --" % g)
#Apply selection based on their converted fitness
selectpop = self.selection(self.pop, popsize)
nextoff = []
while len(nextoff) != popsize:
# Apply crossover and mutation on the offspring
# Select two individuals
offspring = [random.choice(selectpop) for i in xrange(2)]
if random.random() < CXPB: # cross two individuals with probability CXPB
crossoff = self.crossoperate(offspring)
fit_crossoff = evaluate(self.xydata, crossoff.data)# Evaluate the individuals
if random.random() < MUTPB: # mutate an individual with probability MUTPB
muteoff = self.mutation(crossoff,self.bound)
fit_muteoff = evaluate(self.xydata, muteoff.data)# Evaluate the individuals
nextoff.append({'Gene':muteoff,'fitness':fit_muteoff})
# The population is entirely replaced by the offspring
self.pop = nextoff
# Gather all the fitnesses in one list and print the stats
fits = [ind['fitness'] for ind in self.pop]
length = len(self.pop)
mean = sum(fits) / length
sum2 = sum(x*x for x in fits)
std = abs(sum2 / length - mean**2)**0.5
best_ind = self.selectBest(self.pop)
if best_ind['fitness'] < self.bestindividual['fitness']:
self.bestindividual = best_ind
print("Best individual found is %s, %s" % (self.bestindividual['Gene'].data,self.bestindividual['fitness']))
print(" Min fitness of current pop: %s" % min(fits))
print(" Max fitness of current pop: %s" % max(fits))
print(" Avg fitness of current pop: %s" % mean)
print(" Std of currrent pop: %s" % std)
print("-- End of (successful) evolution --")
if __name__ == "__main__":
CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize = 0.8, 0.3, 50, 100#control parameters
up = [64, 64, 64, 64, 64, 64, 64, 64, 64, 64]#upper range for variables
low = [-64, -64, -64, -64, -64, -64, -64, -64, -64, -64]#lower range for variables
parameter = [CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize, low, up]
run = GA(parameter)
run.GA_main()
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。