python队列queue模块详解
队列queue 多应用在多线程应用中,多线程访问共享变量。对于多线程而言,访问共享变量时,队列queue是线程安全的。从queue队列的具体实现中,可以看出queue使用了1个线程互斥锁(pthread.Lock()),以及3个条件标量(pthread.condition()),来保证了线程安全。
queue队列的互斥锁和条件变量,可以参考另一篇文章:python线程中同步锁
queue的用法如下:
import Queque a=[1,2,3] device_que=Queque.queue() device_que.put(a) device=device_que.get()
先看看它的初始化函数__init__(self,maxsize=0):
def __init__(self, maxsize=0): self.maxsize = maxsize self._init(maxsize) # mutex must be held whenever the queue is mutating. All methods # that acquire mutex must release it before returning. mutex # is shared between the three conditions, so acquiring and # releasing the conditions also acquires and releases mutex. self.mutex = _threading.Lock() # Notify not_empty whenever an item is added to the queue; a # thread waiting to get is notified then. self.not_empty = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) # Notify not_full whenever an item is removed from the queue; # a thread waiting to put is notified then. self.not_full = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) # Notify all_tasks_done whenever the number of unfinished tasks # drops to zero; thread waiting to join() is notified to resume self.all_tasks_done = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) self.unfinished_tasks = 0
定义队列时有一个默认的参数maxsize, 如果不指定队列的长度,即manxsize=0,那么队列的长度为无限长,如果定义了大于0的值,那么队列的长度就是maxsize。
self._init(maxsize):使用了python自带的双端队列deque,来存储元素。
self.mutex互斥锁:任何获取队列的状态(empty(),qsize()等),或者修改队列的内容的操作(get,put等)都必须持有该互斥锁。共有两种操作require获取锁,release释放锁。同时该互斥锁被三个共享变量同时享有,即操作conditiond时的require和release操作也就是操作了该互斥锁。
self.not_full条件变量:当队列中有元素添加后,会通知notify其他等待添加元素的线程,唤醒等待require互斥锁,或者有线程从队列中取出一个元素后,通知其它线程唤醒以等待require互斥锁。
self.not empty条件变量:线程添加数据到队列中后,会调用self.not_empty.notify()通知其它线程,唤醒等待require互斥锁后,读取队列。
self.all_tasks_done条件变量:消费者线程从队列中get到任务后,任务处理完成,当所有的队列中的任务处理完成后,会使调用queue.join()的线程返回,表示队列中任务以处理完毕。
queue.put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None)函数:
申请获得互斥锁,获得后,如果队列未满,则向队列中添加数据,并通知notify其它阻塞的某个线程,唤醒等待获取require互斥锁。如果队列已满,则会wait等待。最后处理完成后释放互斥锁。其中还有阻塞block以及非阻塞,超时等逻辑,可以自己看一下:
def put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None):
"""Put an item into the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until a free slot is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Full exception if no free slot was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), put an item on the queue if a free slot
is immediately available, else raise the Full exception ('timeout'
is ignored in that case).
"""
self.not_full.acquire()
try:
if self.maxsize > 0:
if not block:
if self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
raise Full
elif timeout is None:
while self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
self.not_full.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = _time() + timeout
while self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
remaining = endtime - _time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Full
self.not_full.wait(remaining)
self._put(item)
self.unfinished_tasks += 1
self.not_empty.notify()
finally:
self.not_full.release()
queue.get(self, block=True, timeout=None)函数:
从队列中获取任务,并且从队列中移除此任务。首先尝试获取互斥锁,获取成功则队列中get任务,如果此时队列为空,则wait等待生产者线程添加数据。get到任务后,会调用self.not_full.notify()通知生产者线程,队列可以添加元素了。最后释放互斥锁。
def get(self, block=True, timeout=None):
"""Remove and return an item from the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Empty exception if no item was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is immediately
available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is ignored
in that case).
"""
self.not_empty.acquire()
try:
if not block:
if not self._qsize():
raise Empty
elif timeout is None:
while not self._qsize():
self.not_empty.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = _time() + timeout
while not self._qsize():
remaining = endtime - _time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Empty
self.not_empty.wait(remaining)
item = self._get()
self.not_full.notify()
return item
finally:
self.not_empty.release()
queue.put_nowait():无阻塞的向队列中添加任务,当队列为满时,不等待,而是直接抛出full异常,重点是理解block=False:
def put_nowait(self, item): """Put an item into the queue without blocking. Only enqueue the item if a free slot is immediately available. Otherwise raise the Full exception. """ return self.put(item, False)
queue.get_nowait():无阻塞的向队列中get任务,当队列为空时,不等待,而是直接抛出empty异常,重点是理解block=False:
def get_nowait(self): """Remove and return an item from the queue without blocking. Only get an item if one is immediately available. Otherwise raise the Empty exception. """ return self.get(False)
queue.qsize empty full 分别获取队列的长度,是否为空,是否已满等:
def qsize(self): """Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n def empty(self): """Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = not self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n def full(self): """Return True if the queue is full, False otherwise (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = 0 < self.maxsize == self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n
queue.join()阻塞等待队列中任务全部处理完毕,需要配合queue.task_done使用:
def task_done(self):
"""Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete.
Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used to fetch a task,
a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the processing
on the task is complete.
If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all items
have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call was received
for every item that had been put() into the queue).
Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were items
placed in the queue.
"""
self.all_tasks_done.acquire()
try:
unfinished = self.unfinished_tasks - 1
if unfinished <= 0:
if unfinished < 0:
raise ValueError('task_done() called too many times')
self.all_tasks_done.notify_all()
self.unfinished_tasks = unfinished
finally:
self.all_tasks_done.release()
def join(self):
"""Blocks until all items in the Queue have been gotten and processed.
The count of unfinished tasks goes up whenever an item is added to the
queue. The count goes down whenever a consumer thread calls task_done()
to indicate the item was retrieved and all work on it is complete.
When the count of unfinished tasks drops to zero, join() unblocks.
"""
self.all_tasks_done.acquire()
try:
while self.unfinished_tasks:
self.all_tasks_done.wait()
finally:
self.all_tasks_done.release()
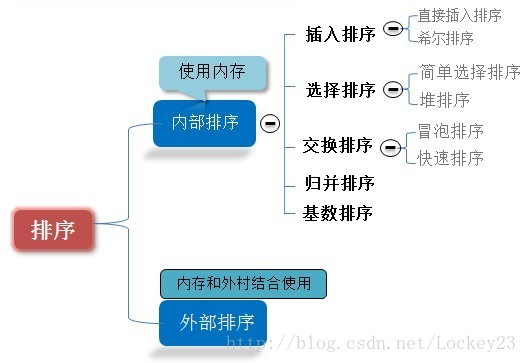
Queue模块除了queue线性安全队列(先进先出),还有优先级队列LifoQueue(后进先出),也就是新添加的先被get到。PriorityQueue具有优先级的队列,即队列中的元素是一个元祖类型,(优先级级别,数据)。
class PriorityQueue(Queue): '''''Variant of Queue that retrieves open entries in priority order (lowest first). Entries are typically tuples of the form: (priority number, data). ''' def _init(self, maxsize): self.queue = [] def _qsize(self, len=len): return len(self.queue) def _put(self, item, heappush=heapq.heappush): heappush(self.queue, item) def _get(self, heappop=heapq.heappop): return heappop(self.queue) class LifoQueue(Queue): '''''Variant of Queue that retrieves most recently added entries first.''' def _init(self, maxsize): self.queue = [] def _qsize(self, len=len): return len(self.queue) def _put(self, item): self.queue.append(item) def _get(self): return self.queue.pop()
至此queue模块介绍完毕,重点是理解互斥锁,条件变量如果协同工作,保证队列的线程安全。
下面是queue的完全代码:
class Queue:
"""Create a queue object with a given maximum size.
If maxsize is <= 0, the queue size is infinite.
"""
def __init__(self, maxsize=0):
self.maxsize = maxsize
self._init(maxsize)
# mutex must be held whenever the queue is mutating. All methods
# that acquire mutex must release it before returning. mutex
# is shared between the three conditions, so acquiring and
# releasing the conditions also acquires and releases mutex.
self.mutex = _threading.Lock()
# Notify not_empty whenever an item is added to the queue; a
# thread waiting to get is notified then.
self.not_empty = _threading.Condition(self.mutex)
# Notify not_full whenever an item is removed from the queue;
# a thread waiting to put is notified then.
self.not_full = _threading.Condition(self.mutex)
# Notify all_tasks_done whenever the number of unfinished tasks
# drops to zero; thread waiting to join() is notified to resume
self.all_tasks_done = _threading.Condition(self.mutex)
self.unfinished_tasks = 0
def task_done(self):
"""Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete.
Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used to fetch a task,
a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the processing
on the task is complete.
If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all items
have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call was received
for every item that had been put() into the queue).
Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were items
placed in the queue.
"""
self.all_tasks_done.acquire()
try:
unfinished = self.unfinished_tasks - 1
if unfinished <= 0:
if unfinished < 0:
raise ValueError('task_done() called too many times')
self.all_tasks_done.notify_all()
self.unfinished_tasks = unfinished
finally:
self.all_tasks_done.release()
def join(self):
"""Blocks until all items in the Queue have been gotten and processed.
The count of unfinished tasks goes up whenever an item is added to the
queue. The count goes down whenever a consumer thread calls task_done()
to indicate the item was retrieved and all work on it is complete.
When the count of unfinished tasks drops to zero, join() unblocks.
"""
self.all_tasks_done.acquire()
try:
while self.unfinished_tasks:
self.all_tasks_done.wait()
finally:
self.all_tasks_done.release()
def qsize(self):
"""Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!)."""
self.mutex.acquire()
n = self._qsize()
self.mutex.release()
return n
def empty(self):
"""Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not reliable!)."""
self.mutex.acquire()
n = not self._qsize()
self.mutex.release()
return n
def full(self):
"""Return True if the queue is full, False otherwise (not reliable!)."""
self.mutex.acquire()
n = 0 < self.maxsize == self._qsize()
self.mutex.release()
return n
def put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None):
"""Put an item into the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until a free slot is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Full exception if no free slot was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), put an item on the queue if a free slot
is immediately available, else raise the Full exception ('timeout'
is ignored in that case).
"""
self.not_full.acquire()
try:
if self.maxsize > 0:
if not block:
if self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
raise Full
elif timeout is None:
while self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
self.not_full.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = _time() + timeout
while self._qsize() == self.maxsize:
remaining = endtime - _time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Full
self.not_full.wait(remaining)
self._put(item)
self.unfinished_tasks += 1
self.not_empty.notify()
finally:
self.not_full.release()
def put_nowait(self, item):
"""Put an item into the queue without blocking.
Only enqueue the item if a free slot is immediately available.
Otherwise raise the Full exception.
"""
return self.put(item, False)
def get(self, block=True, timeout=None):
"""Remove and return an item from the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Empty exception if no item was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is immediately
available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is ignored
in that case).
"""
self.not_empty.acquire()
try:
if not block:
if not self._qsize():
raise Empty
elif timeout is None:
while not self._qsize():
self.not_empty.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = _time() + timeout
while not self._qsize():
remaining = endtime - _time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Empty
self.not_empty.wait(remaining)
item = self._get()
self.not_full.notify()
return item
finally:
self.not_empty.release()
def get_nowait(self):
"""Remove and return an item from the queue without blocking.
Only get an item if one is immediately available. Otherwise
raise the Empty exception.
"""
return self.get(False)
# Override these methods to implement other queue organizations
# (e.g. stack or priority queue).
# These will only be called with appropriate locks held
# Initialize the queue representation
def _init(self, maxsize):
self.queue = deque()
def _qsize(self, len=len):
return len(self.queue)
# Put a new item in the queue
def _put(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
# Get an item from the queue
def _get(self):
return self.queue.popleft()
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。