Python SVM(支持向量机)实现方法完整示例
本文实例讲述了Python SVM(支持向量机)实现方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
运行环境
- Pyhton3
- numpy(科学计算包)
- matplotlib(画图所需,不画图可不必)
计算过程
st=>start: 开始
e=>end: 结束
op1=>operation: 读入数据
op2=>operation: 格式化数据
cond=>condition: 是否达到迭代次数
op3=>operation: 寻找超平面分割最小间隔
ccond=>conditon: 数据是否改变
op4=>operation: 输出结果
st->op1->op2->cond
cond(yes)->op4->e
cond(no)->op3
啊,这markdown flow好难用,我决定就画到这吧=。=
输入样例
/* testSet.txt */ 3.542485 1.977398 -1 3.018896 2.556416 -1 7.551510 -1.580030 1 2.114999 -0.004466 -1 8.127113 1.274372 1 7.108772 -0.986906 1 8.610639 2.046708 1 2.326297 0.265213 -1 3.634009 1.730537 -1 0.341367 -0.894998 -1 3.125951 0.293251 -1 2.123252 -0.783563 -1 0.887835 -2.797792 -1 7.139979 -2.329896 1 1.696414 -1.212496 -1 8.117032 0.623493 1 8.497162 -0.266649 1 4.658191 3.507396 -1 8.197181 1.545132 1 1.208047 0.213100 -1 1.928486 -0.321870 -1 2.175808 -0.014527 -1 7.886608 0.461755 1 3.223038 -0.552392 -1 3.628502 2.190585 -1 7.407860 -0.121961 1 7.286357 0.251077 1 2.301095 -0.533988 -1 -0.232542 -0.547690 -1 3.457096 -0.082216 -1 3.023938 -0.057392 -1 8.015003 0.885325 1 8.991748 0.923154 1 7.916831 -1.781735 1 7.616862 -0.217958 1 2.450939 0.744967 -1 7.270337 -2.507834 1 1.749721 -0.961902 -1 1.803111 -0.176349 -1 8.804461 3.044301 1 1.231257 -0.568573 -1 2.074915 1.410550 -1 -0.743036 -1.736103 -1 3.536555 3.964960 -1 8.410143 0.025606 1 7.382988 -0.478764 1 6.960661 -0.245353 1 8.234460 0.701868 1 8.168618 -0.903835 1 1.534187 -0.622492 -1 9.229518 2.066088 1 7.886242 0.191813 1 2.893743 -1.643468 -1 1.870457 -1.040420 -1 5.286862 -2.358286 1 6.080573 0.418886 1 2.544314 1.714165 -1 6.016004 -3.753712 1 0.926310 -0.564359 -1 0.870296 -0.109952 -1 2.369345 1.375695 -1 1.363782 -0.254082 -1 7.279460 -0.189572 1 1.896005 0.515080 -1 8.102154 -0.603875 1 2.529893 0.662657 -1 1.963874 -0.365233 -1 8.132048 0.785914 1 8.245938 0.372366 1 6.543888 0.433164 1 -0.236713 -5.766721 -1 8.112593 0.295839 1 9.803425 1.495167 1 1.497407 -0.552916 -1 1.336267 -1.632889 -1 9.205805 -0.586480 1 1.966279 -1.840439 -1 8.398012 1.584918 1 7.239953 -1.764292 1 7.556201 0.241185 1 9.015509 0.345019 1 8.266085 -0.230977 1 8.545620 2.788799 1 9.295969 1.346332 1 2.404234 0.570278 -1 2.037772 0.021919 -1 1.727631 -0.453143 -1 1.979395 -0.050773 -1 8.092288 -1.372433 1 1.667645 0.239204 -1 9.854303 1.365116 1 7.921057 -1.327587 1 8.500757 1.492372 1 1.339746 -0.291183 -1 3.107511 0.758367 -1 2.609525 0.902979 -1 3.263585 1.367898 -1 2.912122 -0.202359 -1 1.731786 0.589096 -1 2.387003 1.573131 -1
代码实现
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#!python3
__author__ = 'Wsine'
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import operator
import time
def loadDataSet(fileName):
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
with open(fileName) as fr:
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip().split('\t')
dataMat.append([float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(float(lineArr[2]))
return dataMat, labelMat
def selectJrand(i, m):
j = i
while (j == i):
j = int(random.uniform(0, m))
return j
def clipAlpha(aj, H, L):
if aj > H:
aj = H
if L > aj:
aj = L
return aj
class optStruct:
def __init__(self, dataMatIn, classLabels, C, toler):
self.X = dataMatIn
self.labelMat = classLabels
self.C = C
self.tol = toler
self.m = shape(dataMatIn)[0]
self.alphas = mat(zeros((self.m, 1)))
self.b = 0
self.eCache = mat(zeros((self.m, 2)))
def calcEk(oS, k):
fXk = float(multiply(oS.alphas, oS.labelMat).T * (oS.X * oS.X[k, :].T)) + oS.b
Ek = fXk - float(oS.labelMat[k])
return Ek
def selectJ(i, oS, Ei):
maxK = -1
maxDeltaE = 0
Ej = 0
oS.eCache[i] = [1, Ei]
validEcacheList = nonzero(oS.eCache[:, 0].A)[0]
if (len(validEcacheList)) > 1:
for k in validEcacheList:
if k == i:
continue
Ek = calcEk(oS, k)
deltaE = abs(Ei - Ek)
if (deltaE > maxDeltaE):
maxK = k
maxDeltaE = deltaE
Ej = Ek
return maxK, Ej
else:
j = selectJrand(i, oS.m)
Ej = calcEk(oS, j)
return j, Ej
def updateEk(oS, k):
Ek = calcEk(oS, k)
oS.eCache[k] = [1, Ek]
def innerL(i, oS):
Ei = calcEk(oS, i)
if ((oS.labelMat[i] * Ei < -oS.tol) and (oS.alphas[i] < oS.C)) or ((oS.labelMat[i] * Ei > oS.tol) and (oS.alphas[i] > 0)):
j, Ej = selectJ(i, oS, Ei)
alphaIold = oS.alphas[i].copy()
alphaJold = oS.alphas[j].copy()
if (oS.labelMat[i] != oS.labelMat[j]):
L = max(0, oS.alphas[j] - oS.alphas[i])
H = min(oS.C, oS.C + oS.alphas[j] - oS.alphas[i])
else:
L = max(0, oS.alphas[j] + oS.alphas[i] - oS.C)
H = min(oS.C, oS.alphas[j] + oS.alphas[i])
if (L == H):
# print("L == H")
return 0
eta = 2.0 * oS.X[i, :] * oS.X[j, :].T - oS.X[i, :] * oS.X[i, :].T - oS.X[j, :] * oS.X[j, :].T
if eta >= 0:
# print("eta >= 0")
return 0
oS.alphas[j] -= oS.labelMat[j] * (Ei - Ej) / eta
oS.alphas[j] = clipAlpha(oS.alphas[j], H, L)
updateEk(oS, j)
if (abs(oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold) < 0.00001):
# print("j not moving enough")
return 0
oS.alphas[i] += oS.labelMat[j] * oS.labelMat[i] * (alphaJold - oS.alphas[j])
updateEk(oS, i)
b1 = oS.b - Ei - oS.labelMat[i] * (oS.alphas[i] - alphaIold) * oS.X[i, :] * oS.X[i, :].T - oS.labelMat[j] * (oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold) * oS.X[i, :] * oS.X[j, :].T
b2 = oS.b - Ei - oS.labelMat[i] * (oS.alphas[i] - alphaIold) * oS.X[i, :] * oS.X[j, :].T - oS.labelMat[j] * (oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold) * oS.X[j, :] * oS.X[j, :].T
if (0 < oS.alphas[i]) and (oS.C > oS.alphas[i]):
oS.b = b1
elif (0 < oS.alphas[j]) and (oS.C > oS.alphas[j]):
oS.b = b2
else:
oS.b = (b1 + b2) / 2.0
return 1
else:
return 0
def smoP(dataMatIn, classLabels, C, toler, maxIter, kTup=('lin', 0)):
"""
输入:数据集, 类别标签, 常数C, 容错率, 最大循环次数
输出:目标b, 参数alphas
"""
oS = optStruct(mat(dataMatIn), mat(classLabels).transpose(), C, toler)
iterr = 0
entireSet = True
alphaPairsChanged = 0
while (iterr < maxIter) and ((alphaPairsChanged > 0) or (entireSet)):
alphaPairsChanged = 0
if entireSet:
for i in range(oS.m):
alphaPairsChanged += innerL(i, oS)
# print("fullSet, iter: %d i:%d, pairs changed %d" % (iterr, i, alphaPairsChanged))
iterr += 1
else:
nonBoundIs = nonzero((oS.alphas.A > 0) * (oS.alphas.A < C))[0]
for i in nonBoundIs:
alphaPairsChanged += innerL(i, oS)
# print("non-bound, iter: %d i:%d, pairs changed %d" % (iterr, i, alphaPairsChanged))
iterr += 1
if entireSet:
entireSet = False
elif (alphaPairsChanged == 0):
entireSet = True
# print("iteration number: %d" % iterr)
return oS.b, oS.alphas
def calcWs(alphas, dataArr, classLabels):
"""
输入:alphas, 数据集, 类别标签
输出:目标w
"""
X = mat(dataArr)
labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose()
m, n = shape(X)
w = zeros((n, 1))
for i in range(m):
w += multiply(alphas[i] * labelMat[i], X[i, :].T)
return w
def plotFeature(dataMat, labelMat, weights, b):
dataArr = array(dataMat)
n = shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if int(labelMat[i]) == 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i, 0])
ycord1.append(dataArr[i, 1])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i, 0])
ycord2.append(dataArr[i, 1])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green')
x = arange(2, 7.0, 0.1)
y = (-b[0, 0] * x) - 10 / linalg.norm(weights)
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1'); plt.ylabel('X2')
plt.show()
def main():
trainDataSet, trainLabel = loadDataSet('testSet.txt')
b, alphas = smoP(trainDataSet, trainLabel, 0.6, 0.0001, 40)
ws = calcWs(alphas, trainDataSet, trainLabel)
print("ws = \n", ws)
print("b = \n", b)
plotFeature(trainDataSet, trainLabel, ws, b)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.clock()
main()
end = time.clock()
print('finish all in %s' % str(end - start))
输出样例
ws =
[[ 0.65307162]
[-0.17196128]]
b =
[[-2.89901748]]
finish all in 2.5683854014099112
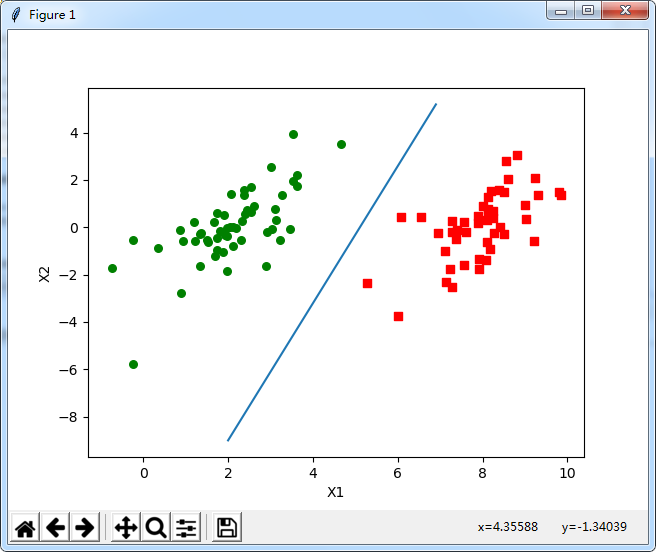
绘图方面还存在一些bug。
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python数学运算技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。