Python Grid使用和布局详解
本文实例为大家分享了Python Grid使用和布局的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
#!/usr/bin/env python
import vtk
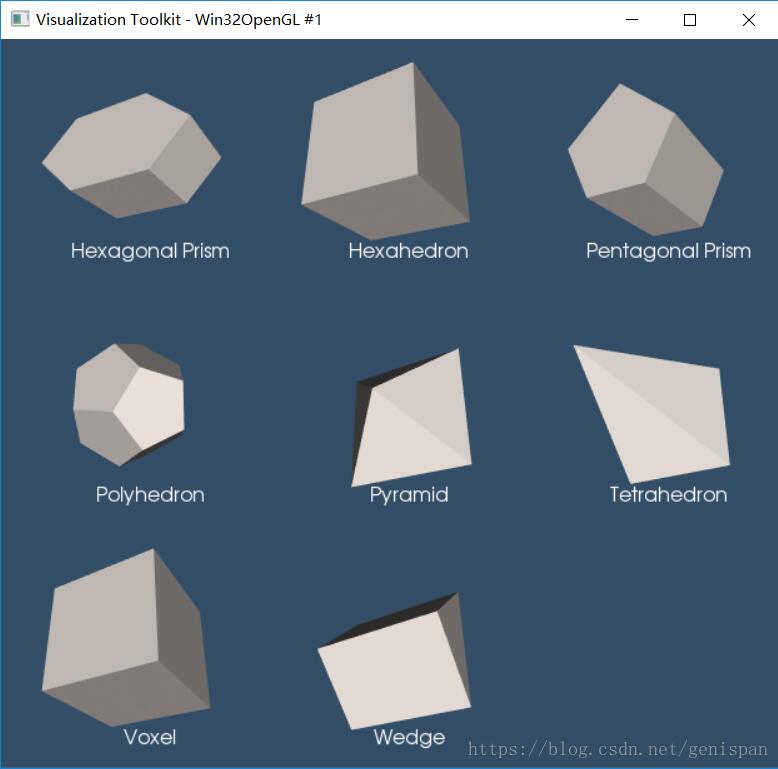
# 这个示例主要用于将不同的图像对象显示到指定的Grid中
def main():
colors = vtk.vtkNamedColors()
# Set the background color.
colors.SetColor("BkgColor", [51, 77, 102, 255])
titles = list()
textMappers = list()
textActors = list()
uGrids = list()
mappers = list()
actors = list()
renderers = list()
uGrids.append(MakeHexagonalPrism())
titles.append('Hexagonal Prism')
uGrids.append(MakeHexahedron())
titles.append('Hexahedron')
uGrids.append(MakePentagonalPrism())
titles.append('Pentagonal Prism')
uGrids.append(MakePolyhedron())
titles.append('Polyhedron')
uGrids.append(MakePyramid())
titles.append('Pyramid')
uGrids.append(MakeTetrahedron())
titles.append('Tetrahedron')
uGrids.append(MakeVoxel())
titles.append('Voxel')
uGrids.append(MakeWedge())
titles.append('Wedge')
renWin = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renWin.SetWindowName('Cell3D Demonstration')
iRen = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iRen.SetRenderWindow(renWin)
# Create one text property for all
textProperty = vtk.vtkTextProperty()
textProperty.SetFontSize(16)
textProperty.SetJustificationToCentered()
# Create and link the mappers actors and renderers together.
# 为每个独立的文本图形对象创建独立的Mapper和Actors,并绑定至每个grid中
for i in range(0, len(uGrids)):
textMappers.append(vtk.vtkTextMapper())
textActors.append(vtk.vtkActor2D())#
mappers.append(vtk.vtkDataSetMapper())
actors.append(vtk.vtkActor())
renderers.append(vtk.vtkRenderer())
mappers[i].SetInputData(uGrids[i])
actors[i].SetMapper(mappers[i])
actors[i].GetProperty().SetColor(
colors.GetColor3d("Seashell"))
renderers[i].AddViewProp(actors[i])
textMappers[i].SetInput(titles[i])
textMappers[i].SetTextProperty(textProperty)
textActors[i].SetMapper(textMappers[i])
textActors[i].SetPosition(120, 16)
renderers[i].AddViewProp(textActors[i])
renWin.AddRenderer(renderers[i])
gridDimensions = 3
rendererSize = 300
renWin.SetSize(rendererSize * gridDimensions,
rendererSize * gridDimensions)
# 渲染图形对象至不同的显示区域
for row in range(0, gridDimensions):
for col in range(0, gridDimensions):
index = row * gridDimensions + col
# (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
viewport = [
float(col) * rendererSize /
(gridDimensions * rendererSize),
float(gridDimensions - (row + 1)) * rendererSize /
(gridDimensions * rendererSize),
float(col + 1) * rendererSize /
(gridDimensions * rendererSize),
float(gridDimensions - row) * rendererSize /
(gridDimensions * rendererSize)]
if index > len(actors) - 1:
# Add a renderer even if there is no actor.
# This makes the render window background all the same color.
ren = vtk.vtkRenderer()
ren.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d("BkgColor"))
ren.SetViewport(viewport)
renWin.AddRenderer(ren)
continue
renderers[index].SetViewport(viewport)
renderers[index].SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d("BkgColor"))
renderers[index].ResetCamera()
renderers[index].GetActiveCamera().Azimuth(30)
renderers[index].GetActiveCamera().Elevation(-30)
renderers[index].GetActiveCamera().Zoom(0.85)
renderers[index].ResetCameraClippingRange()
iRen.Initialize()
renWin.Render()
iRen.Start()
def MakeHexagonalPrism():
"""
3D: hexagonal prism: a wedge with an hexagonal base.
Be careful, the base face ordering is different from wedge.
"""
numberOfVertices = 12
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.5, 0.5, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.5, 0.5, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.5, 0.5, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.5, 0.5, 0.0)
hexagonalPrism = vtk.vtkHexagonalPrism()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
hexagonalPrism.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
ug = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
ug.InsertNextCell(hexagonalPrism.GetCellType(),
hexagonalPrism.GetPointIds())
ug.SetPoints(points)
return ug
def MakeHexahedron():
"""
A regular hexagon (cube) with all faces square and three squares around
each vertex is created below.
Setup the coordinates of eight points
(the two faces must be in counter clockwise
order as viewed from the outside).
As an exercise you can modify the coordinates of the points to create
seven topologically distinct convex hexahedras.
"""
numberOfVertices = 8
# Create the points
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
# Create a hexahedron from the points
hex_ = vtk.vtkHexahedron()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
hex_.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
# Add the points and hexahedron to an unstructured grid
uGrid = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
uGrid.SetPoints(points)
uGrid.InsertNextCell(hex_.GetCellType(), hex_.GetPointIds())
return uGrid
def MakePentagonalPrism():
numberOfVertices = 10
# Create the points
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(11, 10, 10)
points.InsertNextPoint(13, 10, 10)
points.InsertNextPoint(14, 12, 10)
points.InsertNextPoint(12, 14, 10)
points.InsertNextPoint(10, 12, 10)
points.InsertNextPoint(11, 10, 14)
points.InsertNextPoint(13, 10, 14)
points.InsertNextPoint(14, 12, 14)
points.InsertNextPoint(12, 14, 14)
points.InsertNextPoint(10, 12, 14)
# Pentagonal Prism
pentagonalPrism = vtk.vtkPentagonalPrism()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
pentagonalPrism.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
# Add the points and hexahedron to an unstructured grid
uGrid = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
uGrid.SetPoints(points)
uGrid.InsertNextCell(pentagonalPrism.GetCellType(),
pentagonalPrism.GetPointIds())
return uGrid
def MakePolyhedron():
"""
Make a regular dodecahedron. It consists of twelve regular pentagonal
faces with three faces meeting at each vertex.
"""
# numberOfVertices = 20
numberOfFaces = 12
# numberOfFaceVertices = 5
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(1.21412, 0, 1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.375185, 1.1547, 1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.982247, 0.713644, 1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.982247, -0.713644, 1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.375185, -1.1547, 1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.96449, 0, 0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.607062, 1.86835, 0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(-1.58931, 1.1547, 0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(-1.58931, -1.1547, 0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.607062, -1.86835, 0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.58931, 1.1547, -0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.607062, 1.86835, -0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(-1.96449, 0, -0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.607062, -1.86835, -0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(1.58931, -1.1547, -0.375185)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.982247, 0.713644, -1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.375185, 1.1547, -1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(-1.21412, 0, -1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(-0.375185, -1.1547, -1.58931)
points.InsertNextPoint(0.982247, -0.713644, -1.58931)
# Dimensions are [numberOfFaces][numberOfFaceVertices]
dodechedronFace = [
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 5, 10, 6, 1],
[1, 6, 11, 7, 2],
[2, 7, 12, 8, 3],
[3, 8, 13, 9, 4],
[4, 9, 14, 5, 0],
[15, 10, 5, 14, 19],
[16, 11, 6, 10, 15],
[17, 12, 7, 11, 16],
[18, 13, 8, 12, 17],
[19, 14, 9, 13, 18],
[19, 18, 17, 16, 15]
]
dodechedronFacesIdList = vtk.vtkIdList()
# Number faces that make up the cell.
dodechedronFacesIdList.InsertNextId(numberOfFaces)
for face in dodechedronFace:
# Number of points in the face == numberOfFaceVertices
dodechedronFacesIdList.InsertNextId(len(face))
# Insert the pointIds for that face.
[dodechedronFacesIdList.InsertNextId(i) for i in face]
uGrid = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
uGrid.InsertNextCell(vtk.VTK_POLYHEDRON, dodechedronFacesIdList)
uGrid.SetPoints(points)
return uGrid
def MakePyramid():
"""
Make a regular square pyramid.
"""
numberOfVertices = 5
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
p = [
[1.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[-1.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[-1.0, -1.0, 0.0],
[1.0, -1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
]
for pt in p:
points.InsertNextPoint(pt)
pyramid = vtk.vtkPyramid()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
pyramid.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
ug = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
ug.SetPoints(points)
ug.InsertNextCell(pyramid.GetCellType(), pyramid.GetPointIds())
return ug
def MakeTetrahedron():
"""
Make a tetrahedron.
"""
numberOfVertices = 4
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 0, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 0, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 1, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 1, 1)
tetra = vtk.vtkTetra()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
tetra.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
cellArray = vtk.vtkCellArray()
cellArray.InsertNextCell(tetra)
unstructuredGrid = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
unstructuredGrid.SetPoints(points)
unstructuredGrid.SetCells(vtk.VTK_TETRA, cellArray)
return unstructuredGrid
def MakeVoxel():
"""
A voxel is a representation of a regular grid in 3-D space.
"""
numberOfVertices = 8
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 0, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 0, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 1, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 1, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 0, 1)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 0, 1)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 1, 1)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 1, 1)
voxel = vtk.vtkVoxel()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
voxel.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
ug = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
ug.SetPoints(points)
ug.InsertNextCell(voxel.GetCellType(), voxel.GetPointIds())
return ug
def MakeWedge():
"""
A wedge consists of two triangular ends and three rectangular faces.
"""
numberOfVertices = 6
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 1, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, 0, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(0, .5, .5)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 1, 0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, 0.0, 0.0)
points.InsertNextPoint(1, .5, .5)
wedge = vtk.vtkWedge()
for i in range(0, numberOfVertices):
wedge.GetPointIds().SetId(i, i)
ug = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid()
ug.SetPoints(points)
ug.InsertNextCell(wedge.GetCellType(), wedge.GetPointIds())
return ug
def WritePNG(renWin, fn, magnification=1):
"""
Screenshot
Write out a png corresponding to the render window.
:param: renWin - the render window.
:param: fn - the file name.
:param: magnification - the magnification.
"""
windowToImageFilter = vtk.vtkWindowToImageFilter()
windowToImageFilter.SetInput(renWin)
windowToImageFilter.SetMagnification(magnification)
# Record the alpha (transparency) channel
# windowToImageFilter.SetInputBufferTypeToRGBA()
windowToImageFilter.SetInputBufferTypeToRGB()
# Read from the back buffer
windowToImageFilter.ReadFrontBufferOff()
windowToImageFilter.Update()
writer = vtk.vtkPNGWriter()
writer.SetFileName(fn)
writer.SetInputConnection(windowToImageFilter.GetOutputPort())
writer.Write()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。