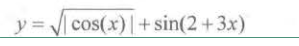python实现决策树分类(2)
在上一篇文章中,我们已经构建了决策树,接下来可以使用它用于实际的数据分类。在执行数据分类时,需要决策时以及标签向量。程序比较测试数据和决策树上的数值,递归执行直到进入叶子节点。
这篇文章主要使用决策树分类器就行分类,数据集采用UCI数据库中的红酒,白酒数据,主要特征包括12个,主要有非挥发性酸,挥发性酸度, 柠檬酸, 残糖含量,氯化物, 游离二氧化硫, 总二氧化硫,密度, pH,硫酸盐,酒精, 质量等特征。
下面是具体代码的实现:
#coding :utf-8
'''
2017.6.26 author :Erin
function: "decesion tree" ID3
'''
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from math import log
import operator
import random
def load_data():
red = [line.strip().split(';') for line in open('e:/a/winequality-red.csv')]
white = [line.strip().split(';') for line in open('e:/a/winequality-white.csv')]
data=red+white
random.shuffle(data) #打乱data
x_train=data[:800]
x_test=data[800:]
features=['fixed','volatile','citric','residual','chlorides','free','total','density','pH','sulphates','alcohol','quality']
return x_train,x_test,features
def cal_entropy(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet:
label = featVec[-1]
if label not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[label] = 0
labelCounts[label] += 1
entropy = 0.0
for key in labelCounts.keys():
p_i = float(labelCounts[key]/numEntries)
entropy -= p_i * log(p_i,2)#log(x,10)表示以10 为底的对数
return entropy
def split_data(data,feature_index,value):
'''
划分数据集
feature_index:用于划分特征的列数,例如“年龄”
value:划分后的属性值:例如“青少年”
'''
data_split=[]#划分后的数据集
for feature in data:
if feature[feature_index]==value:
reFeature=feature[:feature_index]
reFeature.extend(feature[feature_index+1:])
data_split.append(reFeature)
return data_split
def choose_best_to_split(data):
'''
根据每个特征的信息增益,选择最大的划分数据集的索引特征
'''
count_feature=len(data[0])-1#特征个数4
#print(count_feature)#4
entropy=cal_entropy(data)#原数据总的信息熵
#print(entropy)#0.9402859586706309
max_info_gain=0.0#信息增益最大
split_fea_index = -1#信息增益最大,对应的索引号
for i in range(count_feature):
feature_list=[fe_index[i] for fe_index in data]#获取该列所有特征值
#######################################
# print(feature_list)
unqval=set(feature_list)#去除重复
Pro_entropy=0.0#特征的熵
for value in unqval:#遍历改特征下的所有属性
sub_data=split_data(data,i,value)
pro=len(sub_data)/float(len(data))
Pro_entropy+=pro*cal_entropy(sub_data)
#print(Pro_entropy)
info_gain=entropy-Pro_entropy
if(info_gain>max_info_gain):
max_info_gain=info_gain
split_fea_index=i
return split_fea_index
##################################################
def most_occur_label(labels):
#sorted_label_count[0][0] 次数最多的类标签
label_count={}
for label in labels:
if label not in label_count.keys():
label_count[label]=0
else:
label_count[label]+=1
sorted_label_count = sorted(label_count.items(),key = operator.itemgetter(1),reverse = True)
return sorted_label_count[0][0]
def build_decesion_tree(dataSet,featnames):
'''
字典的键存放节点信息,分支及叶子节点存放值
'''
featname = featnames[:] ################
classlist = [featvec[-1] for featvec in dataSet] #此节点的分类情况
if classlist.count(classlist[0]) == len(classlist): #全部属于一类
return classlist[0]
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #分完了,没有属性了
return Vote(classlist) #少数服从多数
# 选择一个最优特征进行划分
bestFeat = choose_best_to_split(dataSet)
bestFeatname = featname[bestFeat]
del(featname[bestFeat]) #防止下标不准
DecisionTree = {bestFeatname:{}}
# 创建分支,先找出所有属性值,即分支数
allvalue = [vec[bestFeat] for vec in dataSet]
specvalue = sorted(list(set(allvalue))) #使有一定顺序
for v in specvalue:
copyfeatname = featname[:]
DecisionTree[bestFeatname][v] = build_decesion_tree(split_data(dataSet,bestFeat,v),copyfeatname)
return DecisionTree
def classify(Tree, featnames, X):
classLabel=''
root = list(Tree.keys())[0]
firstDict = Tree[root]
featindex = featnames.index(root) #根节点的属性下标
#classLabel='0'
for key in firstDict.keys(): #根属性的取值,取哪个就走往哪颗子树
if X[featindex] == key:
if type(firstDict[key]) == type({}):
classLabel = classify(firstDict[key],featnames,X)
else:
classLabel = firstDict[key]
return classLabel
if __name__ == '__main__':
x_train,x_test,features=load_data()
split_fea_index=choose_best_to_split(x_train)
newtree=build_decesion_tree(x_train,features)
#print(newtree)
#classLabel=classify(newtree, features, ['7.4','0.66','0','1.8','0.075','13','40','0.9978','3.51','0.56','9.4','5'] )
#print(classLabel)
count=0
for test in x_test:
label=classify(newtree, features,test)
if(label==test[-1]):
count=count+1
acucy=float(count/len(x_test))
print(acucy)
测试的准确率大概在0.7左右。至此决策树分类算法结束。本文代码地址
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。