TensorFlow实现模型评估
我们需要评估模型预测值来评估训练的好坏。
模型评估是非常重要的,随后的每个模型都有模型评估方式。使用TensorFlow时,需要把模型评估加入到计算图中,然后在模型训练完后调用模型评估。
在训练模型过程中,模型评估能洞察模型算法,给出提示信息来调试、提高或者改变整个模型。但是在模型训练中并不是总需要模型评估,我们将展示如何在回归算法和分类算法中使用它。
训练模型之后,需要定量评估模型的性能如何。在理想情况下,评估模型需要一个训练数据集和测试数据集,有时甚至需要一个验证数据集。
想评估一个模型时就得使用大批量数据点。如果完成批量训练,我们可以重用模型来预测批量数据点。但是如果要完成随机训练,就不得不创建单独的评估器来处理批量数据点。
分类算法模型基于数值型输入预测分类值,实际目标是1和0的序列。我们需要度量预测值与真实值之间的距离。分类算法模型的损失函数一般不容易解释模型好坏,所以通常情况是看下准确预测分类的结果的百分比。
不管算法模型预测的如何,我们都需要测试算法模型,这点相当重要。在训练数据和测试数据上都进行模型评估,以搞清楚模型是否过拟合。
# TensorFlowm模型评估
#
# This code will implement two models. The first
# is a simple regression model, we will show how to
# call the loss function, MSE during training, and
# output it after for test and training sets.
#
# The second model will be a simple classification
# model. We will also show how to print percent
# classified correctly during training and after
# for both the test and training sets.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# 创建计算图
sess = tf.Session()
# 回归例子:
# We will create sample data as follows:
# x-data: 100 random samples from a normal ~ N(1, 0.1)
# target: 100 values of the value 10.
# We will fit the model:
# x-data * A = target
# 理论上, A = 10.
# 声明批量大小
batch_size = 25
# 创建数据集
x_vals = np.random.normal(1, 0.1, 100)
y_vals = np.repeat(10., 100)
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# 八二分训练/测试数据 train/test = 80%/20%
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
# 创建变量 (one model parameter = A)
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
# 增加操作到计算图
my_output = tf.matmul(x_data, A)
# 增加L2损失函数到计算图
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(my_output - y_target))
# 创建优化器
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.02)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 迭代运行
# 如果在损失函数中使用的模型输出结果经过转换操作,例如,sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits()函数,
# 为了精确计算预测结果,别忘了在模型评估中也要进行转换操作。
for i in range(100):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals_train[rand_index]])
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
if (i+1)%25==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)))
print('Loss = ' + str(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})))
# 评估准确率(loss)
mse_test = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_test]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])})
mse_train = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_train]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])})
print('MSE on test:' + str(np.round(mse_test, 2)))
print('MSE on train:' + str(np.round(mse_train, 2)))
# 分类算法案例
# We will create sample data as follows:
# x-data: sample 50 random values from a normal = N(-1, 1)
# + sample 50 random values from a normal = N(1, 1)
# target: 50 values of 0 + 50 values of 1.
# These are essentially 100 values of the corresponding output index
# We will fit the binary classification model:
# If sigmoid(x+A) < 0.5 -> 0 else 1
# Theoretically, A should be -(mean1 + mean2)/2
# 重置计算图
ops.reset_default_graph()
# 加载计算图
sess = tf.Session()
# 声明批量大小
batch_size = 25
# 创建数据集
x_vals = np.concatenate((np.random.normal(-1, 1, 50), np.random.normal(2, 1, 50)))
y_vals = np.concatenate((np.repeat(0., 50), np.repeat(1., 50)))
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, None], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, None], dtype=tf.float32)
# 分割数据集 train/test = 80%/20%
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
# 创建变量 (one model parameter = A)
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(mean=10, shape=[1]))
# Add operation to graph
# Want to create the operstion sigmoid(x + A)
# Note, the sigmoid() part is in the loss function
my_output = tf.add(x_data, A)
# 增加分类损失函数 (cross entropy)
xentropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=my_output, labels=y_target))
# Create Optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(xentropy)
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 运行迭代
for i in range(1800):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = [x_vals_train[rand_index]]
rand_y = [y_vals_train[rand_index]]
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
if (i+1)%200==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)))
print('Loss = ' + str(sess.run(xentropy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})))
# 评估预测
# 用squeeze()函数封装预测操作,使得预测值和目标值有相同的维度。
y_prediction = tf.squeeze(tf.round(tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(x_data, A))))
# 用equal()函数检测是否相等,
# 把得到的true或false的boolean型张量转化成float32型,
# 再对其取平均值,得到一个准确度值。
correct_prediction = tf.equal(y_prediction, y_target)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
acc_value_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: [x_vals_test], y_target: [y_vals_test]})
acc_value_train = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: [x_vals_train], y_target: [y_vals_train]})
print('Accuracy on train set: ' + str(acc_value_train))
print('Accuracy on test set: ' + str(acc_value_test))
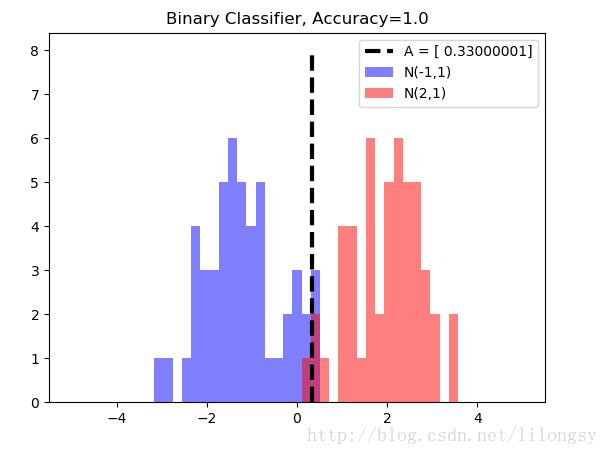
# 绘制分类结果
A_result = -sess.run(A)
bins = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
plt.hist(x_vals[0:50], bins, alpha=0.5, label='N(-1,1)', color='white')
plt.hist(x_vals[50:100], bins[0:50], alpha=0.5, label='N(2,1)', color='red')
plt.plot((A_result, A_result), (0, 8), 'k--', linewidth=3, label='A = '+ str(np.round(A_result, 2)))
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Binary Classifier, Accuracy=' + str(np.round(acc_value_test, 2)))
plt.show()
输出:
Step #25 A = [[ 5.79096079]] Loss = 16.8725 Step #50 A = [[ 8.36085415]] Loss = 3.60671 Step #75 A = [[ 9.26366138]] Loss = 1.05438 Step #100 A = [[ 9.58914948]] Loss = 1.39841 MSE on test:1.04 MSE on train:1.13 Step #200 A = [ 5.83126402] Loss = 1.9799 Step #400 A = [ 1.64923656] Loss = 0.678205 Step #600 A = [ 0.12520729] Loss = 0.218827 Step #800 A = [-0.21780498] Loss = 0.223919 Step #1000 A = [-0.31613481] Loss = 0.234474 Step #1200 A = [-0.33259964] Loss = 0.237227 Step #1400 A = [-0.28847221] Loss = 0.345202 Step #1600 A = [-0.30949864] Loss = 0.312794 Step #1800 A = [-0.33211425] Loss = 0.277342 Accuracy on train set: 0.9625 Accuracy on test set: 1.0
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。