python实现多层感知器
写了个多层感知器,用bp梯度下降更新,拟合正弦曲线,效果凑合。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sigmod(z):
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
class mlp(object):
def __init__(self, lr=0.1, lda=0.0, te=1e-5, epoch=100, size=None):
self.learningRate = lr
self.lambda_ = lda
self.thresholdError = te
self.maxEpoch = epoch
self.size = size
self.W = []
self.b = []
self.init()
def init(self):
for i in xrange(len(self.size)-1):
self.W.append(np.mat(np.random.uniform(-0.5, 0.5, size=(self.size[i+1], self.size[i]))))
self.b.append(np.mat(np.random.uniform(-0.5, 0.5, size=(self.size[i+1], 1))))
def forwardPropagation(self, item=None):
a = [item]
for wIndex in xrange(len(self.W)):
a.append(sigmod(self.W[wIndex]*a[-1]+self.b[wIndex]))
"""
print "-----------------------------------------"
for i in a:
print i.shape,
print
for i in self.W:
print i.shape,
print
for i in self.b:
print i.shape,
print
print "-----------------------------------------"
"""
return a
def backPropagation(self, label=None, a=None):
# print "backPropagation--------------------begin"
delta = [(a[-1]-label)*a[-1]*(1.0-a[-1])]
for i in xrange(len(self.W)-1):
abc = np.multiply(a[-2-i], 1-a[-2-i])
cba = np.multiply(self.W[-1-i].T*delta[-1], abc)
delta.append(cba)
"""
print "++++++++++++++delta++++++++++++++++++++"
print "len(delta):", len(delta)
for ii in delta:
print ii.shape,
print "\n======================================="
"""
for j in xrange(len(delta)):
ads = delta[j]*a[-2-j].T
# print self.W[-1-j].shape, ads.shape, self.b[-1-j].shape, delta[j].shape
self.W[-1-j] = self.W[-1-j]-self.learningRate*(ads+self.lambda_*self.W[-1-j])
self.b[-1-j] = self.b[-1-j]-self.learningRate*delta[j]
"""print "=======================================1234"
for ij in self.b:
print ij.shape,
print
"""
# print "backPropagation--------------------finish"
error = 0.5*(a[-1]-label)**2
return error
def train(self, input_=None, target=None, show=10):
for ep in xrange(self.maxEpoch):
error = []
for itemIndex in xrange(input_.shape[1]):
a = self.forwardPropagation(input_[:, itemIndex])
e = self.backPropagation(target[:, itemIndex], a)
error.append(e[0, 0])
tt = sum(error)/len(error)
if tt < self.thresholdError:
print "Finish {0}: ".format(ep), tt
return
elif ep % show == 0:
print "epoch {0}: ".format(ep), tt
def sim(self, inp=None):
return self.forwardPropagation(item=inp)[-1]
if __name__ == "__main__":
tt = np.arange(0, 6.28, 0.01)
labels = np.zeros_like(tt)
print tt.shape
"""
for po in xrange(tt.shape[0]):
if tt[po] < 4:
labels[po] = 0.0
elif 8 > tt[po] >= 4:
labels[po] = 0.25
elif 12 > tt[po] >= 8:
labels[po] = 0.5
elif 16 > tt[po] >= 12:
labels[po] = 0.75
else:
labels[po] = 1.0
"""
tt = np.mat(tt)
labels = np.sin(tt)*0.5+0.5
labels = np.mat(labels)
model = mlp(lr=0.2, lda=0.0, te=1e-5, epoch=500, size=[1, 6, 6, 6, 1])
print tt.shape, labels.shape
print len(model.W), len(model.b)
print
model.train(input_=tt, target=labels, show=10)
sims = [model.sim(tt[:, idx])[0, 0] for idx in xrange(tt.shape[1])]
xx = tt.tolist()[0]
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xx, labels.tolist()[0], xx, sims, 'r')
plt.show()
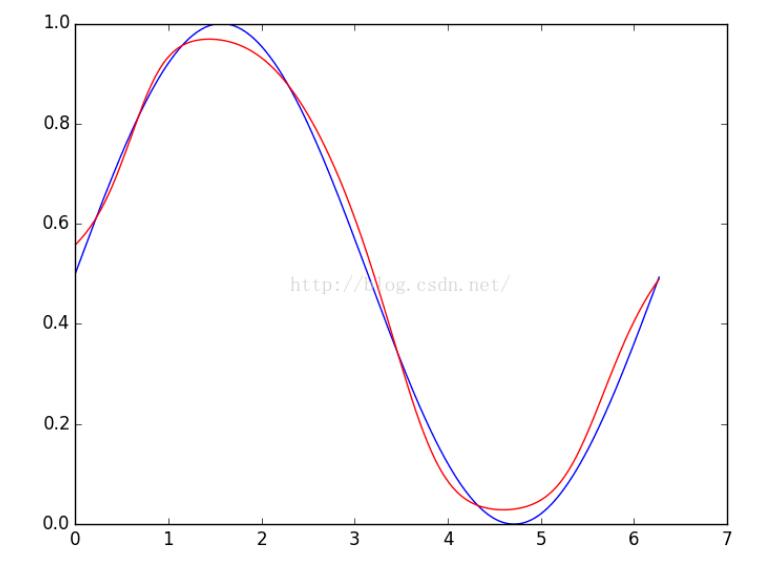
效果图:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。