利用python实现对web服务器的目录探测的方法
一、python
Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
python 是一门简单易学的语言,并且功能强大也很灵活,在渗透测试中的应用广泛,让我们一起打造属于自己的渗透测试工具
二、web服务器的目录探测脚本打造
1、在渗透时如果能发现web服务器中的webshell,渗透是不是就可以变的简单一点尼
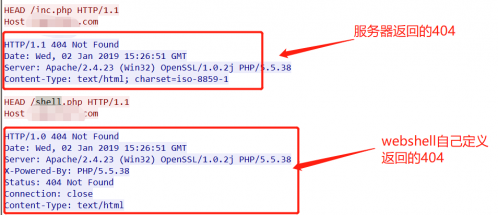
通常情况下御剑深受大家的喜爱,但是今天在测试的时候webshell不知道为什么御剑扫描不到
仔细查看是webshell有防爬功能,是检测User-Agent头,如果没有就回返回一个自己定义的404页面
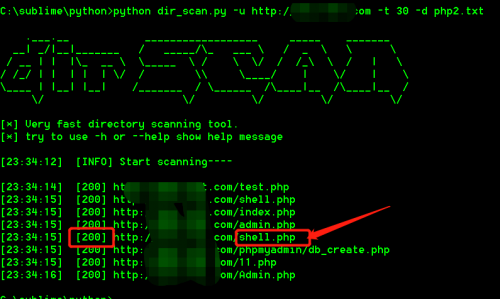
1、先来看看工具效果
2、利用python读取扫描的目录字典
def get_url(path):
with open(path, "r", encoding='ISO-8859-1') as f:
for url in f.readlines():
url_list.append(url.strip())
return url_list
3、利用 python 的 requests 库对web目标服务器进行目录探测
def Go_scan(url):
while not queue.empty():
url_path = queue.get(timeout=1)
new_url = url + url_path
res = requests.get(new_url, headers=headers, timeout=5)
#print(res.status_code)
status_code = "[" + str(res.status_code) + "]"
if str(res.status_code) != "404":
print(get_time(), status_code, new_url)
4、利用 python 的 threading 库对探测进行线程的设置
def thread(Number,url):
threadlist = []
for pwd in url_list:
queue.put(pwd)
for x in range(Number):
t = threading.Thread(target=Go_scan, args=(url,))
threadlist.append(t)
for t in threadlist:
t.start()
5、利用 python 的 argparse 库进行对自己的工具进行封装
def main():
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print_banner()
exit(1)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.RawTextHelpFormatter,
epilog='''\
use examples:
python dir_scan.py -u [url]http://www.test.com[/url] -d /root/dir.txt
python dir_scan.py -u [url]http://www.test.com[/url] -t 30 -d /root/dir.txt
''')
parser.add_argument("-u","--url", help="scan target address", dest='url')
parser.add_argument("-t","--thread", help="Number of threads", default="20", type=int, dest='thread')
parser.add_argument("-d","--Dictionaries", help="Dictionary of Blasting Loading",
dest="Dictionaries")
总结
各位大哥有意见或者建议尽管提,文章哪里不对的话会改的,小弟定会虚心学习最后附上全部源码供大佬指教
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import requests
import threading
import argparse,sys
import time,os
from queue import Queue
url_list = []
queue = Queue()
headers = {
'Connection':'keep-alive',
'Accept':'*/*',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN',
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2; rv:16.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/16.0'
}
def print_banner():
banner = r"""
.___.__ __________________ _____ _______
__| _/|__|_______ / _____/\_ ___ \ / _ \ \ \
/ __ | | |\_ __ \ \_____ \ / \ \/ / /_\ \ / | \
/ /_/ | | | | | \/ / \\ \____/ | \/ | \
\____ | |__| |__| /_______ / \______ /\____|__ /\____|__ /
\/ \/ \/ \/ \/
[*] Very fast directory scanning tool.
[*] try to use -h or --help show help message
"""
print(banner)
def get_time():
return '[' + time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) + '] '
def get_url(path):
with open(path, "r", encoding='ISO-8859-1') as f:
for url in f.readlines():
url_list.append(url.strip())
return url_list
def Go_scan(url):
while not queue.empty():
url_path = queue.get(timeout=1)
new_url = url + url_path
res = requests.get(new_url, headers=headers, timeout=5)
#print(res.status_code)
status_code = "[" + str(res.status_code) + "]"
if str(res.status_code) != "404":
print(get_time(), status_code, new_url)
def thread(Number,url):
threadlist = []
for pwd in url_list:
queue.put(pwd)
for x in range(Number):
t = threading.Thread(target=Go_scan, args=(url,))
threadlist.append(t)
for t in threadlist:
t.start()
def main():
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print_banner()
exit(1)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.RawTextHelpFormatter,
epilog='''\
use examples:
python dir_scan.py -u [url]http://www.test.com[/url] -d /root/dir.txt
python dir_scan.py -u [url]http://www.test.com[/url] -t 30 -d /root/dir.txt
''')
parser.add_argument("-u","--url", help="scan target address", dest='url')
parser.add_argument("-t","--thread", help="Number of threads", default="20", type=int, dest='thread')
parser.add_argument("-d","--Dictionaries", help="Dictionary of Blasting Loading",
dest="Dictionaries")
args = parser.parse_args()
Number =args.thread
url = args.url
url_path = args.Dictionaries
print_banner()
get_url(url_path)
print(get_time(), "[INFO] Start scanning----\n")
time.sleep(2)
thread(Number,url)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。