python 将有序数组转换为二叉树的方法
题目:将[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]存储到二叉树,原数组有序,转换为二叉排序树。
二叉排序树的特点:当前节点的左子树上的所有节点都小于该节点,右子树上的所有节点都小于该节点。
二叉排序也称为二叉查找树。
我的实现思路:
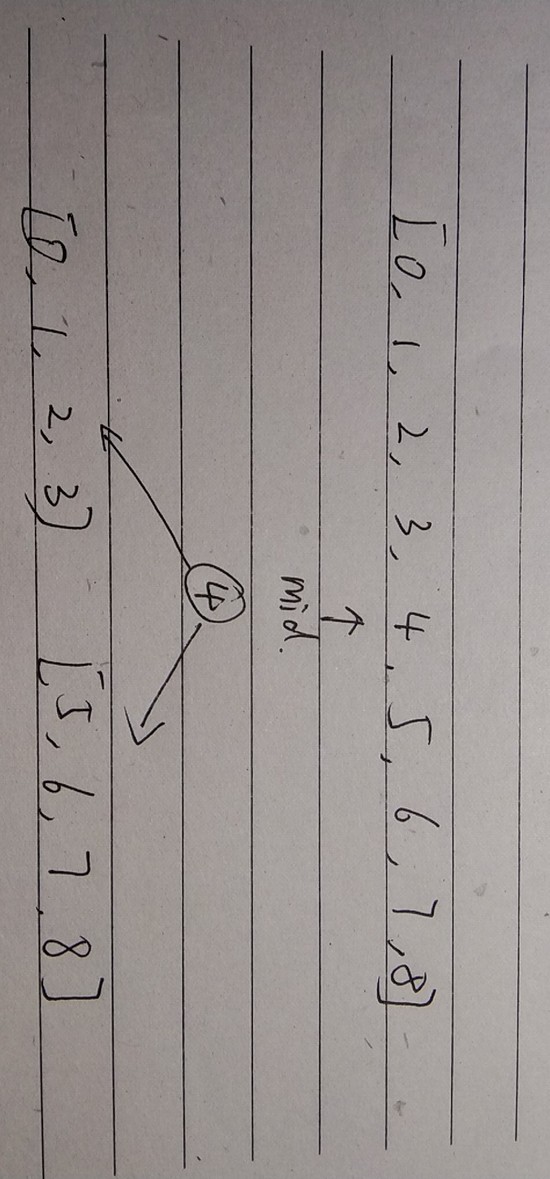
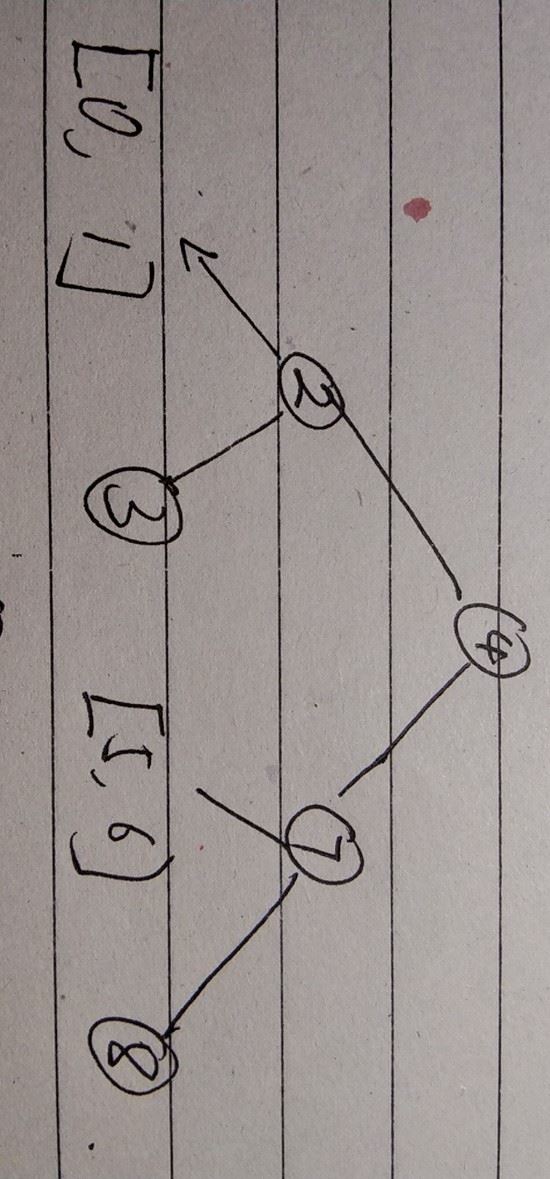
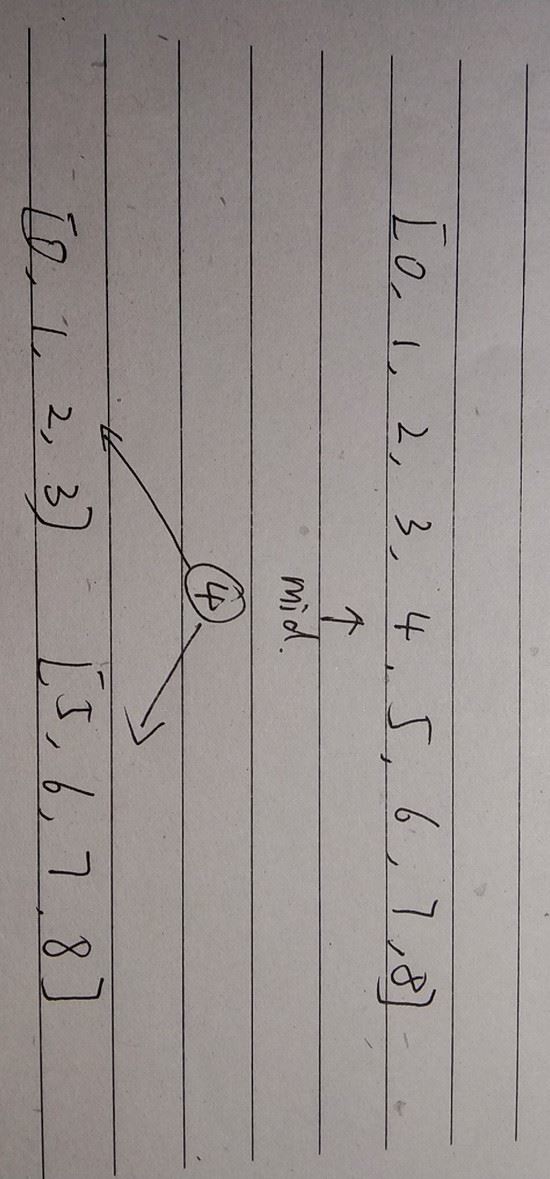
取有序数组的中间节点作为根节点,将数组分为左右两个部分,对左右两个子数组做相同的操作,递归的实现。
图示:
1
2
3
代码实现:
def array_to_bitree(array):
#判断arr是否为空
if len(array)==0:
return BiTNode(array[0])
mid=len(array)//2 # 有序数组的中间元素的下标
#print(mid)
#start=0 # 数组第一个元素的下标
#end=-1 # 数组最后一个元素的下标
if len(array)>0:
#将中间元素作为二叉树的根
root=BiTNode(array[mid])
#如果左边的元素个数不为零,则递归调用函数,生成左子树
if len(array[:mid])>0:
root.left_child = arrayToBiTree(array[:mid])
#如果右边的元素个数不为零,则递归调用函数,生成左子树
if len(array[mid+1:])>0:
root.right_child = arrayToBiTree(array[mid+1:])
return root
我们调用前面写的三种遍历方法看一看,我们构造的树是否正确:
#将[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]存储到二叉树
if __name__ == '__main__':
#先构造一个有序数组、链表
arr=[]
for i in range(10):
arr.append(i)
print(arr)
#调用函数
BT=arrayToBiTree(arr)
#前序遍历二叉树
print("前序")
print_tree_pre_order(BT)
# 中序遍历二叉树
print("中序")
print_tree_mid_order(BT)
# 后序遍历二叉树
print("后序")
print_tree_after_order(BT)
输出:

根据这三种遍历结果可以判断出二叉树的结构,结果和前面的是一样的,代码如下:
#定义二叉树结点类型
class BiTNode:
"""docstring for BiTNode"""
def __init__(self,arg):
self.data = arg
self.left_child = None
self.right_child = None
#前序遍历
def print_tree_pre_order(root):
#先判断二叉树是否为空
#if root.left_child is None and root.right_child is None:
if root is None:
return root
#先根
print(root.data)
#再左
if root.left_child is not None:
print_tree_pre_order(root.left_child)
#再右
if root.right_child is not None:
print_tree_pre_order(root.right_child)
#中序遍历二叉树
def print_tree_mid_order(root):
#先判断二叉树是否为空,当左右节点都为空时
if root is None:
return
#中序遍历 左根右
#遍历左子树
if root.left_child is not None:
print_tree_mid_order(root.left_child)
#遍历根节点
print(root.data)
#遍历右子树
if root.right_child is not None:
print_tree_mid_order(root.right_child)
#后序遍历
def print_tree_after_order(root):
#先判断二叉树是否为空
if root is None:
return root
#再左
if root.left_child is not None:
print_tree_after_order(root.left_child)
#再右
if root.right_child is not None:
print_tree_after_order(root.right_child)
#先根
print(root.data)
def array_to_bitree(array):
#判断arr是否为空
if len(array)==0:
return BiTNode(array[0])
mid=len(array)//2 # 有序数组的中间元素的下标
#print(mid)
#start=0 # 数组第一个元素的下标
#end=-1 # 数组最后一个元素的下标
if len(array)>0:
#将中间元素作为二叉树的根
root=BiTNode(array[mid])
#如果左边的元素个数不为零,则递归调用函数,生成左子树
if len(array[:mid])>0:
root.left_child = array_to_bitree(array[:mid])
#如果右边的元素个数不为零,则递归调用函数,生成左子树
if len(array[mid+1:])>0:
root.right_child = array_to_bitree(array[mid+1:])
return root
#将[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]存储到二叉树
if __name__ == '__main__':
#先构造一个有序数组、链表
arr=[]
for i in range(9):
arr.append(i)
print(arr)
#调用函数
BT=array_to_bitree(arr)
#前序遍历二叉树
print("前序")
print_tree_pre_order(BT)
# 中序遍历二叉树
print("中序")
print_tree_mid_order(BT)
# 后序遍历二叉树
print("后序")
print_tree_after_order(BT)
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。