django admin后台添加导出excel功能示例代码
Django功能强大不单在于他先进的编程理念,很多现有的功能模块更是可以直接拿来使用,比如这个牛掰的admin模块,可以作为一个很好的信息登记管理系统。
admin模块中的actioin是可以自定义添加的,比如这次要介绍的导出excel功能,就可以在action中触发。
本文将详细介绍如何导出admin中录入的数据为excel,可以直接提交给你的leader观看。
首先我们要安装 xlwt 这个工具模块:
pip install xlwt
import的准备 修改admin.py:
#-*-coding:utf-8 -*- from django.contrib import admin from .models import * from django.http import StreamingHttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect import xlwt import os from io import BytesIO
添加action:
class testAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = ('a_name','b_level','...')
actions = ["export_excel",]
...
export_excel.short_description = "导出Excel文件"
添加后的效果如图:
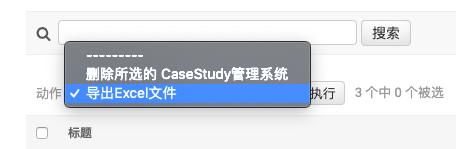
接下来编写导出excel的功能函数:
def export_excel(self, request, queryset): #三个参数必不可少,queryset是你要导出的文件名
for i in queryset: #这个for循环是为了在多选的时候只导出第一个文件,避免多个被同时导出
filenames = str(i)
break;
response = HttpResponse(content_type='application/vnd.ms-excel')
for i in Case_Study.objects.all().filter(a_name = filenames):
filename = i.a_name
filename = filename.encode('gb2312') #为了能将导出的excel命名为中文,必须转成gb2312
typess = 'attachment;filename='+filename+'.xls' #这一步命名导出的excel,为登记的case名称
response['Content-Disposition'] = typess
#print typess
# 创建一个文件对象
wb = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf8')
# 创建一个sheet对象
sheet = wb.add_sheet('casestudy',cell_overwrite_ok=True) #创建的sheet名称为casestudy,注意如果想要开启覆盖写入,必须将overwrite功能开启
接下来是定义字体和表格样式:
# 接下里是定义表格的样式,如果你想对不同的表格定义不同的样式只能采用下面这种方式,否则将会默认成一种格式,即使定义了不同的变量,也会影响全局变量
style_heading = xlwt.easyxf("""
font: # 字体设置
name Microsoft YaHei, # 定义字体为微软雅黑
colour_index black, # 字体颜色为黑色
bold off, # 不加粗
height 200; #字体大小 此处的200实际对应的字号是10号
align: # 对齐方式设置
wrap off, #自动换行 关闭
vert center, #上下居中
horiz center; #左右居中
pattern: #表格样式设置
pattern solid,
fore-colour white; # 表格颜色 白色
borders: # 表格外框设置
left THIN, #THIN 为实线
right THIN,
top THIN,
bottom THIN;
""")
style_playback = xlwt.easyxf("""
font:
name Microsoft YaHei,
colour_index black,
bold off,
height 200;
align:
wrap 1, # 此处设置为1时表示开启自动换行
vert center,
horiz left;
pattern:
pattern solid,
fore-colour white;
borders:
left THIN,
right THIN,
top THIN,
bottom THIN;
""")
style_time_s = xlwt.easyxf("""
font:
name Microsoft YaHei,
colour_index black,
bold off,
height 200;
align:
wrap off,
vert center,
horiz center;
pattern:
pattern solid,
fore-colour white;
borders:
left THIN,
right THIN,
top THIN,
bottom THIN;
""",num_format_str='YYYY-MM-DD') # 设置时间格式样式为 2019-03-01
style_time = style_heading
style_time.num_format_str = 'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm' # 设置时间格式样式为 2019-03-01 17:30
接下来是合并单元格,这个是一个比较细的工作:
#合并单元格 顺序是从0开始
sheet.write_merge(0, 0, 1, 3,) # 参数说明为 从第0行到第0行的第1列到第3列合并
sheet.write_merge(2, 3, 1, 5,) # 参数说明为 从第2行到第3行的第1列到第5列合并
#多行执行相同的合并可以写个for循环
for i in range(6,12):
sheet.write_merge(i,i,1,3,) #相当于在6到12行的第1列到第3列分别合并 如果这个逻辑绕不明白可以自己实践一下
接下来是添加边框,因为合并了单元格不等于自动加边框,导致导出的表格里有未加边框的情况,所以只能先行添加好
#添加边框,可以用两个for来实现,具体逻辑可自行根据实际情况修改
for i in range(6,12):
for j in range(1,6):
sheet.write(i,j,'',style_heading)
接下来是写入表头
# 写入文件标题
sheet.write(0,0,'标题',style_heading)
sheet.write(0,4,'故障等级',style_heading)
sheet.write(1,0,'开始时间',style_heading)
sheet.write(1,2,'结束时间',style_heading)
sheet.write(1,4,'持续时间',style_heading)
sheet.write(2,0,'影响描述',style_heading)
...
接下来是定义表格的宽度和高度
sheet.col(0).width = 3333
sheet.col(1).width = 6666
...
sheet.row(0).height_mismatch = True # 高度可不依赖字体大小定义,定义高度时最好开启此选项
sheet.row(0).height = 40*20
...
for i in range(7,12): # 也可以通过for循环批量定义高度或宽度
sheet.row(i).height_mismatch = True
sheet.row(i).height = 40*20
接下来是写入数据
#写入数据
for i in Case_Study.objects.all().filter(a_name = filenames): # 查询要写入的数据
sheet.write(0,1,i.a_name,style_playback)
sheet.write(0,5,i.b_level,style_heading)
sheet.write(1,1,i.d_starttime,style_time)
sheet.write(1,3,i.e_endttime,style_time)
...
最后是写出道IO并返回
# 写出到IO
output = BytesIO()
wb.save(output)
# 重新定位到开始
output.seek(0)
response.write(output.getvalue())
return response
export_excel.short_description = "导出Excel文件"
admin.site.register(test,testAdmin)
以上就是导出excel的全部代码,由于导出的是xls格式,很多excel新的功能比如瀑布图,雷达图等是没有的,需要各位手动复制表格到 xlsx格式中修改,避免采坑。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。