numpy.where() 用法详解
numpy.where (condition[, x, y])
numpy.where() 有两种用法:
1. np.where(condition, x, y)
满足条件(condition),输出x,不满足输出y。
如果是一维数组,相当于[xv if c else yv for (c,xv,yv) in zip(condition,x,y)]
>>> aa = np.arange(10)
>>> np.where(aa,1,-1)
array([-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) # 0为False,所以第一个输出-1
>>> np.where(aa > 5,1,-1)
array([-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
>>> np.where([[True,False], [True,True]], # 官网上的例子
[[1,2], [3,4]],
[[9,8], [7,6]])
array([[1, 8],
[3, 4]])
上面这个例子的条件为[[True,False], [True,False]],分别对应最后输出结果的四个值。第一个值从[1,9]中选,因为条件为True,所以是选1。第二个值从[2,8]中选,因为条件为False,所以选8,后面以此类推。类似的问题可以再看个例子:
>>> a = 10
>>> np.where([[a > 5,a < 5], [a == 10,a == 7]],
[["chosen","not chosen"], ["chosen","not chosen"]],
[["not chosen","chosen"], ["not chosen","chosen"]])
array([['chosen', 'chosen'],
['chosen', 'chosen']], dtype='<U10')
2. np.where(condition)
只有条件 (condition),没有x和y,则输出满足条件 (即非0) 元素的坐标 (等价于numpy.nonzero)。这里的坐标以tuple的形式给出,通常原数组有多少维,输出的tuple中就包含几个数组,分别对应符合条件元素的各维坐标。
>>> a = np.array([2,4,6,8,10]) >>> np.where(a > 5) # 返回索引 (array([2, 3, 4]),) >>> a[np.where(a > 5)] # 等价于 a[a>5] array([ 6, 8, 10]) >>> np.where([[0, 1], [1, 0]]) (array([0, 1]), array([1, 0]))
上面这个例子条件中[[0,1],[1,0]]的真值为两个1,各自的第一维坐标为[0,1],第二维坐标为[1,0] 。
下面看个复杂点的例子:
>>> a = np.arange(27).reshape(3,3,3)
>>> a
array([[[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8]],
[[ 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17]],
[[18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26]]])
>>> np.where(a > 5)
(array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]),
array([2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2]),
array([0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2]))
# 符合条件的元素为
[ 6, 7, 8]],
[[ 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17]],
[[18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26]]]
所以np.where会输出每个元素的对应的坐标,因为原数组有三维,所以tuple中有三个数组。
1、numpy.where的返回结果
numpy.where调用方式为numpy.where(condition,1,2)
满足条件的位置上返回结果1,不满足的位置上返回结果2
例如通过where()函数将a数组中负值设为0,正值不变

如果没有指定返回结果,只有查找条件则返回满足条件的位置。返回的结果是一个元组(tuple),包含两个数组,第一个数组纪录的是行,第二个数组纪录的是列。

可以使用zip函数将返回的位置组成一个个坐标对,方便调用。zip函数直接返回的是一个对象,可以用过for循环遍历出里面的元素,也可以使用list直接列出所有坐标对元素。
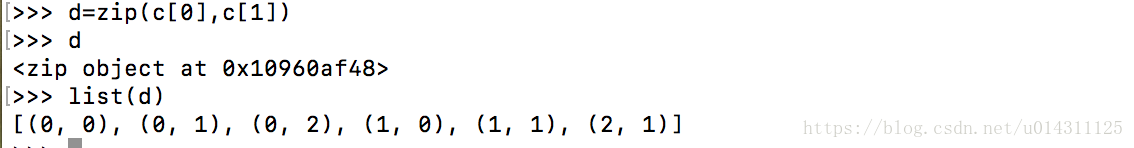
2、numpy.where多条件查询
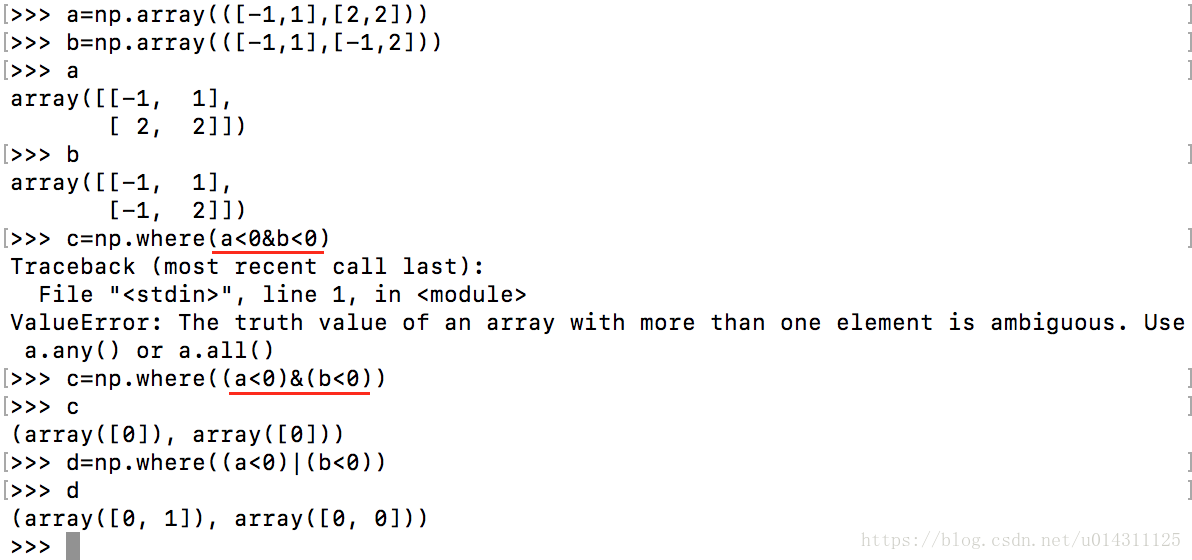
与: numpy.where((con1)*(con2))或者用&
或:numpy.where((con1)|(con2)) (重点:多条件查询时条件一定要用括号!一定要用括号!一定要用括号!)
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。