python机器学习库scikit-learn:SVR的基本应用
scikit-learn是python的第三方机器学习库,里面集成了大量机器学习的常用方法。例如:贝叶斯,svm,knn等。
scikit-learn的官网 : http://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html点击打开链接
SVR是支持向量回归(support vector regression)的英文缩写,是支持向量机(SVM)的重要的应用分支。
scikit-learn中提供了基于libsvm的SVR解决方案。
PS:libsvm是台湾大学林智仁教授等开发设计的一个简单、易于使用和快速有效的SVM模式识别与回归的软件包。
我们自己随机产生一些值,然后使用sin函数进行映射,使用SVR对数据进行拟合
from __future__ import division
import time
import numpy as np
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
#############################################################################
# 生成随机数据
X = 5 * rng.rand(10000, 1)
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
# 在标签中对每50个结果标签添加噪声
y[::50] += 2 * (0.5 - rng.rand(int(X.shape[0]/50)))
X_plot = np.linspace(0, 5, 100000)[:, None]
#############################################################################
# 训练SVR模型
#训练规模
train_size = 100
#初始化SVR
svr = GridSearchCV(SVR(kernel='rbf', gamma=0.1), cv=5,
param_grid={"C": [1e0, 1e1, 1e2, 1e3],
"gamma": np.logspace(-2, 2, 5)})
#记录训练时间
t0 = time.time()
#训练
svr.fit(X[:train_size], y[:train_size])
svr_fit = time.time() - t0
t0 = time.time()
#测试
y_svr = svr.predict(X_plot)
svr_predict = time.time() - t0
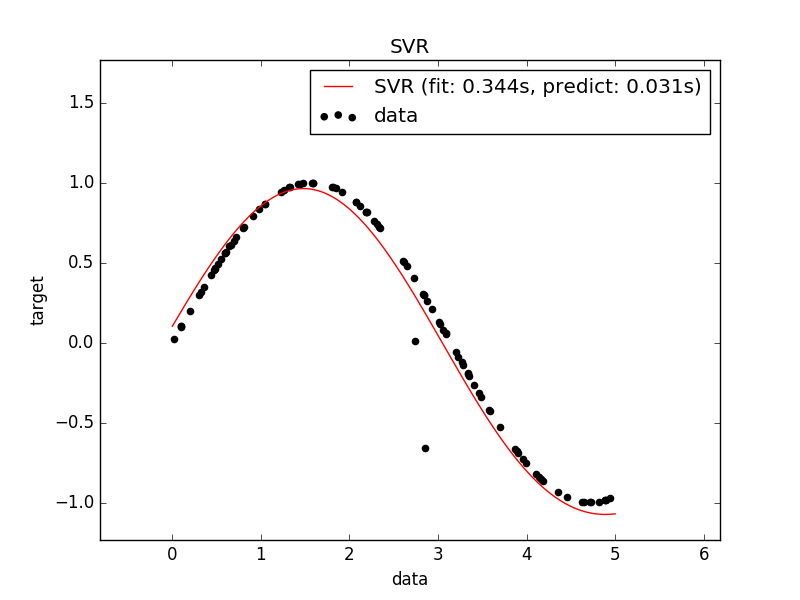
然后我们对结果进行可视化处理
#############################################################################
# 对结果进行显示
plt.scatter(X[:100], y[:100], c='k', label='data', zorder=1)
plt.hold('on')
plt.plot(X_plot, y_svr, c='r',
label='SVR (fit: %.3fs, predict: %.3fs)' % (svr_fit, svr_predict))
plt.xlabel('data')
plt.ylabel('target')
plt.title('SVR versus Kernel Ridge')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
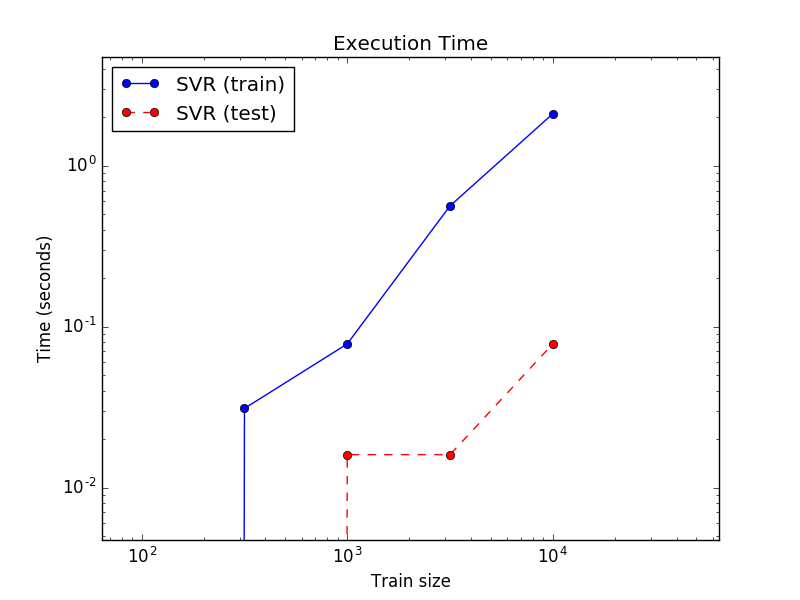
##############################################################################
# 对训练和测试的过程耗时进行可视化
X = 5 * rng.rand(1000000, 1)
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
y[::50] += 2 * (0.5 - rng.rand(int(X.shape[0]/50)))
sizes = np.logspace(1, 4, 7)
for name, estimator in {
"SVR": SVR(kernel='rbf', C=1e1, gamma=10)}.items():
train_time = []
test_time = []
for train_test_size in sizes:
t0 = time.time()
estimator.fit(X[:int(train_test_size)], y[:int(train_test_size)])
train_time.append(time.time() - t0)
t0 = time.time()
estimator.predict(X_plot[:1000])
test_time.append(time.time() - t0)
plt.plot(sizes, train_time, 'o-', color="b" if name == "SVR" else "g",
label="%s (train)" % name)
plt.plot(sizes, test_time, 'o--', color="r" if name == "SVR" else "g",
label="%s (test)" % name)
plt.xscale("log")
plt.yscale("log")
plt.xlabel("Train size")
plt.ylabel("Time (seconds)")
plt.title('Execution Time')
plt.legend(loc="best")
################################################################################
# 对学习过程进行可视化
plt.figure()
svr = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=1e1, gamma=0.1)
train_sizes, train_scores_svr, test_scores_svr = \
learning_curve(svr, X[:100], y[:100], train_sizes=np.linspace(0.1, 1, 10),
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
plt.plot(train_sizes, -test_scores_svr.mean(1), 'o-', color="r",
label="SVR")
plt.xlabel("Train size")
plt.ylabel("Mean Squared Error")
plt.title('Learning curves')
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
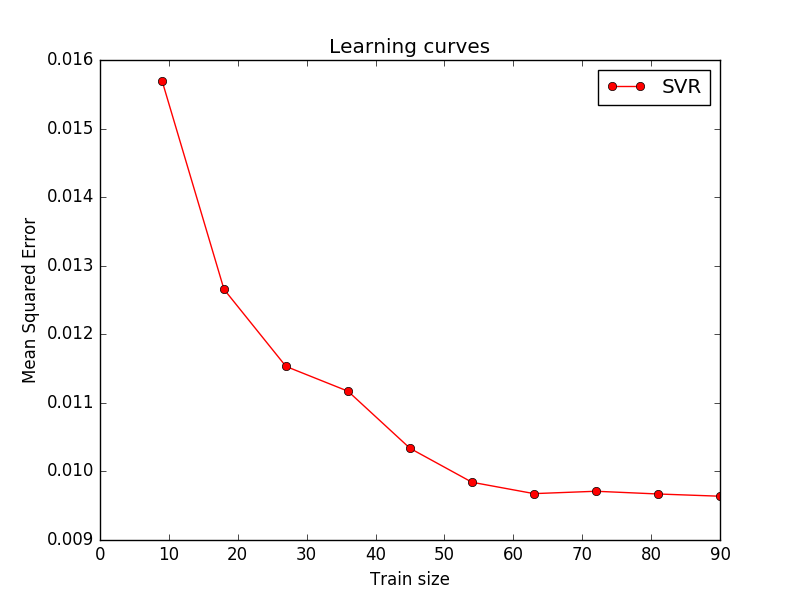
看见了熟悉的LOSS下降图,我仿佛又回到了学生时代。。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。