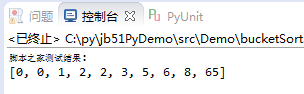
python使用递归的方式建立二叉树
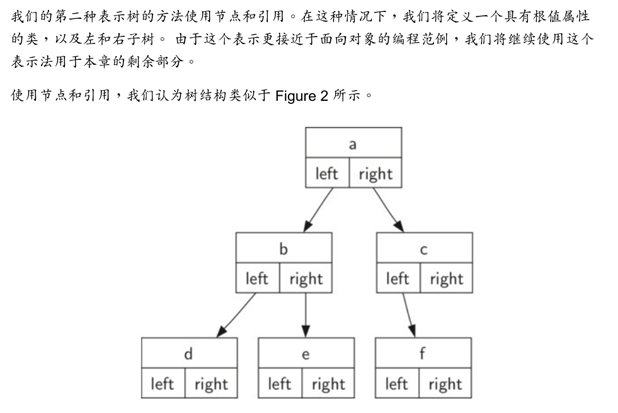
树和图的数据结构,就很有意思啦。
# coding = utf-8
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self, root_obj):
self.key = root_obj
self.left_child = None
self.right_child = None
def insert_left(self, new_node):
node = BinaryTree(new_node)
if self.left_child is None:
self.left_child = node
else:
node.left_child = self.left_child
self.left_child = node
def insert_right(self, new_node):
node = BinaryTree(new_node)
if self.right_child is None:
self.right_child = node
else:
node.right_child = self.right_child
self.right_child = node
def get_right_child(self):
return self.right_child
def get_left_child(self):
return self.left_child
def set_root_val(self, obj):
self.key = obj
def get_root_val(self):
return self.key
root = BinaryTree('a')
print(root.get_root_val())
print(root.get_left_child())
root.insert_left('b')
print(root.get_left_child())
print(root.get_left_child().get_root_val())
root.insert_right('c')
print(root.get_right_child())
print(root.get_right_child().get_root_val())
root.get_right_child().set_root_val('hello')
print(root.get_right_child().get_root_val())
C:\Users\Sahara\.virtualenvs\test\Scripts\python.exe C:/Users/Sahara/PycharmProjects/test/python_search.py a None <__main__.BinaryTree object at 0x00000000024139B0> b <__main__.BinaryTree object at 0x00000000024139E8> c hello Process finished with exit code 0
Python实现二叉树遍历的递归和非递归算法
前序遍历
# -----------前序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def pre_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
print(T.root, end=' ')
self.pre_order_recursive(T.lchild)
self.pre_order_recursive(T.rchild)
# 非递归算法
def pre_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助栈实现前驱遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
while T or len(stack) > 0:
if T:
stack.append(T)
print(T.root, end=' ')
T = T.lchild
else:
T = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
T = T.rchild
中序遍历
# -----------中序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def mid_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
self.mid_order_recursive(T.lchild)
print(T.root, end=' ')
self.mid_order_recursive(T.rchild)
# 非递归算法
def mid_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助栈实现中序遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
while T or len(stack) > 0:
if T:
stack.append(T)
T = T.lchild
else:
T = stack.pop()
print(T.root, end=' ')
T = T.rchild
后序遍历
# -----------后序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def post_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
self.post_order_recursive(T.lchild)
self.post_order_recursive(T.rchild)
print(T.root, end=' ')
# 非递归算法
def post_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助两个栈实现后序遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack1 = []
stack2 = []
stack1.append(T)
while stack1:
node = stack1.pop()
if node.lchild:
stack1.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild:
stack1.append(node.rchild)
stack2.append(node)
while stack2:
print(stack2.pop().root, end=' ')
return
层次遍历
# -----------层次遍历 ------------
def level_order(self, T):
"""借助队列(其实还是一个栈)实现层次遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
stack.append(T)
while stack:
node = stack.pop(0) # 实现先进先出
print(node.root, end=' ')
if node.lchild:
stack.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild:
stack.append(node.rchild)
完整代码
class NodeTree:
def __init__(self, root=None, lchild=None, rchild=None):
"""创建二叉树
Argument:
lchild: BinTree
左子树
rchild: BinTree
右子树
Return:
Tree
"""
self.root = root
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
class BinTree:
# -----------前序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def pre_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
print(T.root, end=' ')
self.pre_order_recursive(T.lchild)
self.pre_order_recursive(T.rchild)
# 非递归算法
def pre_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助栈实现前驱遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
while T or len(stack) > 0:
if T:
stack.append(T)
print(T.root, end=' ')
T = T.lchild
else:
T = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
T = T.rchild
# -----------中序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def mid_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
self.mid_order_recursive(T.lchild)
print(T.root, end=' ')
self.mid_order_recursive(T.rchild)
# 非递归算法
def mid_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助栈实现中序遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
while T or len(stack) > 0:
if T:
stack.append(T)
T = T.lchild
else:
T = stack.pop()
print(T.root, end=' ')
T = T.rchild
# -----------后序遍历 ------------
# 递归算法
def post_order_recursive(self, T):
if T == None:
return
self.post_order_recursive(T.lchild)
self.post_order_recursive(T.rchild)
print(T.root, end=' ')
# 非递归算法
def post_order_non_recursive(self, T):
"""借助两个栈实现后序遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack1 = []
stack2 = []
stack1.append(T)
while stack1:
node = stack1.pop()
if node.lchild:
stack1.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild:
stack1.append(node.rchild)
stack2.append(node)
while stack2:
print(stack2.pop().root, end=' ')
return
# -----------层次遍历 ------------
def level_order(self, T):
"""借助队列(其实还是一个栈)实现层次遍历
"""
if T == None:
return
stack = []
stack.append(T)
while stack:
node = stack.pop(0) # 实现先进先出
print(node.root, end=' ')
if node.lchild:
stack.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild:
stack.append(node.rchild)
# ----------- 前序遍历序列、中序遍历序列 —> 重构二叉树 ------------
def tree_by_pre_mid(self, pre, mid):
if len(pre) != len(mid) or len(pre) == 0 or len(mid) == 0:
return
T = NodeTree(pre[0])
index = mid.index(pre[0])
T.lchild = self.tree_by_pre_mid(pre[1:index + 1], mid[:index])
T.rchild = self.tree_by_pre_mid(pre[index + 1:], mid[index + 1:])
return T
# ----------- 后序遍历序列、中序遍历序列 —> 重构二叉树 ------------
def tree_by_post_mid(self, post, mid):
if len(post) != len(mid) or len(post) == 0 or len(mid) == 0:
return
T = NodeTree(post[-1])
index = mid.index(post[-1])
T.lchild = self.tree_by_post_mid(post[:index], mid[:index])
T.rchild = self.tree_by_post_mid(post[index:-1], mid[index + 1:])
return T
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ----------- 测试:前序、中序、后序、层次遍历 -----------
# 创建二叉树
nodeTree = NodeTree(1,
lchild=NodeTree(2,
lchild=NodeTree(4,
rchild=NodeTree(7))),
rchild=NodeTree(3,
lchild=NodeTree(5),
rchild=NodeTree(6)))
T = BinTree()
print('前序遍历递归\t')
T.pre_order_recursive(nodeTree) # 前序遍历-递归
print('\n')
print('前序遍历非递归\t')
T.pre_order_non_recursive(nodeTree) # 前序遍历-非递归
print('\n')
print('中序遍历递归\t')
T.mid_order_recursive(nodeTree) # 中序遍历-递归
print('\n')
print('中序遍历非递归\t')
T.mid_order_non_recursive(nodeTree) # 中序遍历-非递归
print('\n')
print('后序遍历递归\t')
T.post_order_recursive(nodeTree) # 后序遍历-递归
print('\n')
print('后序遍历非递归\t')
T.post_order_non_recursive(nodeTree) # 后序遍历-非递归
print('\n')
print('层次遍历\t')
T.level_order(nodeTree) # 层次遍历
print('\n')
print('==========================================================================')
# ----------- 测试:由遍历序列构造二叉树 -----------
T = BinTree()
pre = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I']
mid = ['B', 'C', 'A', 'E', 'D', 'G', 'H', 'F', 'I']
post = ['C', 'B', 'E', 'H', 'G', 'I', 'F', 'D', 'A']
newT_pre_mid = T.tree_by_pre_mid(pre, mid) # 由前序序列、中序序列构造二叉树
T.post_order_recursive(newT_pre_mid) # 获取后序序列
print('\n')
newT_post_mid = T.tree_by_post_mid(post, mid) # 由后序序列、中序序列构造二叉树
T.pre_order_recursive(newT_post_mid) # 获取前序序列
运行结果
前序遍历递归
1 2 4 7 3 5 6前序遍历非递归
1 2 4 7 3 5 6中序遍历递归
4 7 2 1 5 3 6中序遍历非递归
4 7 2 1 5 3 6后序遍历递归
7 4 2 5 6 3 1后序遍历非递归
7 4 2 5 6 3 1层次遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7==========================================================================
C B E H G I F D AA B C D E F G H I
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。