Python 中PyQt5 点击主窗口弹出另一个窗口的实现方法
1.先使用Qt designer设计两个窗口,一个是主窗口,一个是子窗口
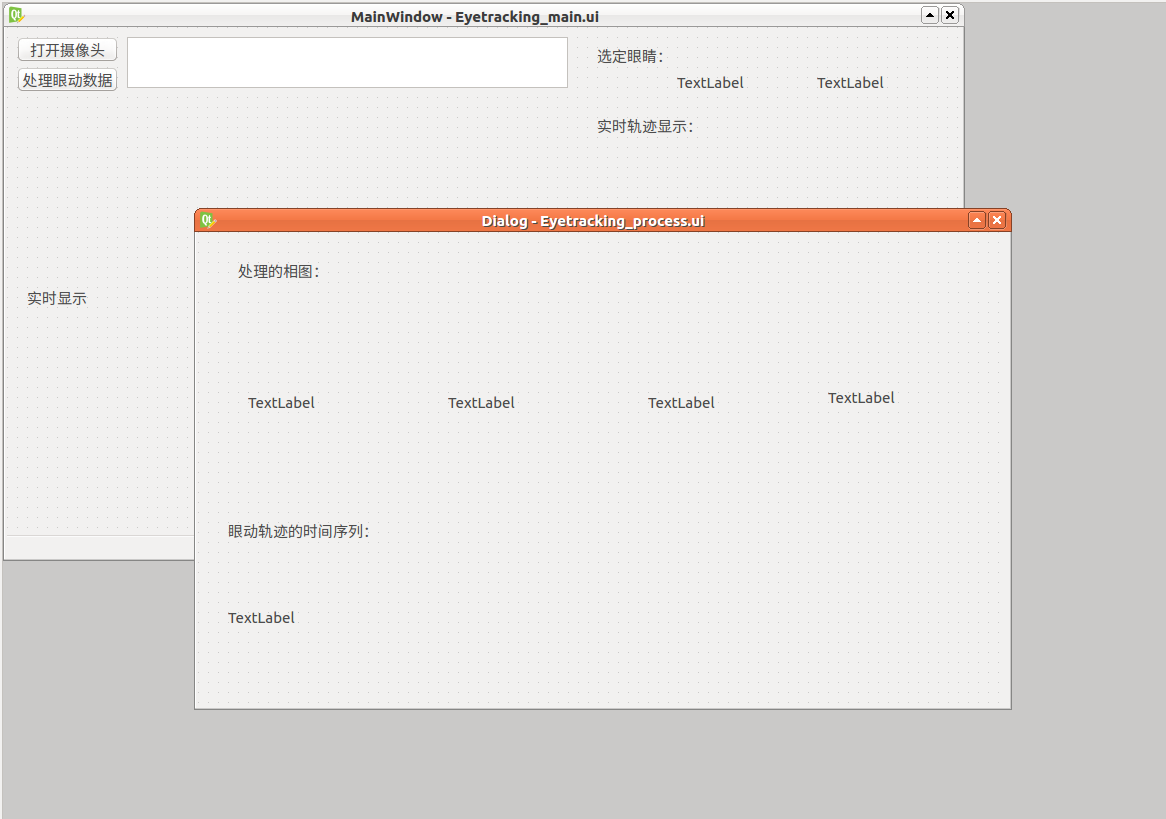 |
其中主窗口是新建-Main Window,子窗口是Dialog窗体。
两个窗口不能是同一类型,否则会崩溃。
并保存为EyeTracking_main.ui和EyeTracking_process.ui(因为我在做眼动追踪,因此窗体命名与此相关,后同),使用UIC工具转成.py文件。
2.写一个驱动函数调用两个窗体
主窗体Eyetracking_main.py
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(954, 530)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.toolButton = QtWidgets.QToolButton(self.centralwidget)
self.toolButton.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(10, 40, 101, 25)) self.toolButton.setObjectName("toolButton")
...1234567891011
子窗体Eyetracking_process.py
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_Dialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setObjectName("Dialog")
Dialog.resize(810, 474)
self.label_5 = QtWidgets.QLabel(Dialog)
self.label_5.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(630, 90, 151, 151))
self.label_5.setObjectName("label_5")
self.label_2 = QtWidgets.QLabel(Dialog)
self.label_2.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(250, 90, 171, 161))
self.label_2.setObjectName
("label_2")
...12345678910111213
将驱动函数命名为EyeTracking_ui.py
from Eyetracking_main import *
from Eyetracking_process import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QMainWindow,QDialog
import sys
class parentWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)
self.main_ui = Ui_MainWindow()
self.main_ui.setupUi(self)
class childWindow(QDialog):
def __init__(self):
QDialog.__init__(self)
self.child=Ui_Dialog()
self.child.setupUi(self)
if __name__=='__main__':
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
window=parentWindow()
child=childWindow()
#通过toolButton将两个窗体关联
btn=window.main_ui.toolButton
btn.clicked.connect(child.show)
# 显示
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
因为后续还要在各个窗体操作,因此将主窗口与子窗口各自实例化在parentWindow和childWindow两个类中,这两个类各自继承了QMainWindow和QDialog的父类:
class parentWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)#QMainWindow的初始化
self.main_ui = Ui_MainWindow()#主窗口的实例化
self.main_ui.setupUi(self)
class childWindow(QDialog):
def __init__(self):
QDialog.__init__(self)
self.child=Ui_Dialog()#子窗口的实例化
self.child.setupUi(self)
后面分别再把两个窗口实例化给window和child:
window=parentWindow() child=childWindow()
通过定义按钮意义将两个窗体关联起来:
btn=window.main_ui.toolButton btn.clicked.connect(child.show)
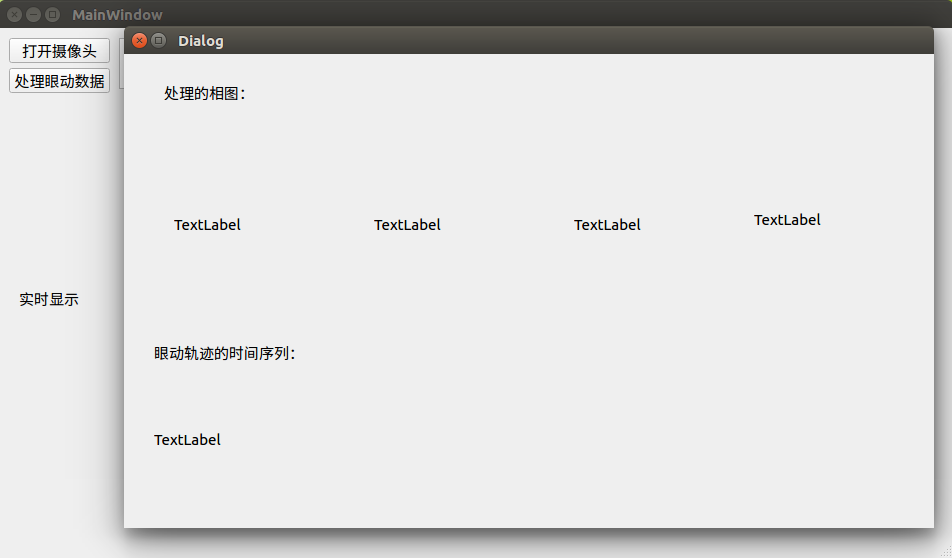
表示当按钮按下时,子窗口显示。
如下图,当点击“处理眼动数据”,弹出处理处理窗体:
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Python 中PyQt5 点击主窗口弹出另一个窗口的实现方法,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对【听图阁-专注于Python设计】网站的支持!
如果你觉得本文对你有帮助,欢迎转载,烦请注明出处,谢谢!