pandas.DataFrame的pivot()和unstack()实现行转列
示例:有如下表需要进行行转列:
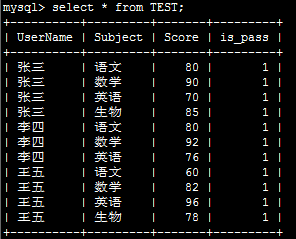
代码如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
import MySQLdb
from warnings import filterwarnings
# 由于create table if not exists总会抛出warning,因此使用filterwarnings消除
filterwarnings('ignore', category = MySQLdb.Warning)
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import sys
if sys.version_info.major<3:
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")
# 此脚本适用于python2和python3
host,port,user,passwd,db,charset="192.168.1.193",3306,"leo","mysql","test","utf8"
def get_df():
global host,port,user,passwd,db,charset
conn_config={"host":host, "port":port, "user":user, "passwd":passwd, "db":db,"charset":charset}
conn = MySQLdb.connect(**conn_config)
result_df=pd.read_sql('select UserName,Subject,Score from TEST',conn)
return result_df
def pivot(result_df):
df_pivoted_init=result_df.pivot('UserName','Subject','Score')
df_pivoted = df_pivoted_init.reset_index() # 将行索引也作为DataFrame值的一部分,以方便存储数据库
return df_pivoted_init,df_pivoted
# 返回的两个DataFrame,一个是以姓名作index的,一个是以数字序列作index,前者用于unpivot,后者用于save_to_mysql
def unpivot(df_pivoted_init):
# unpivot需要进行df_pivoted_init二维表格的行、列索引遍历,需要拼SQL因此不能使用save_to_mysql存数据,这里使用SQL和MySQLdb接口存
insert_sql="insert into test_unpivot(UserName,Subject,Score) values "
# 处理值为NaN的情况
df_pivoted_init=df_pivoted_init.fillna(0)
for col in df_pivoted_init.columns:
for index in df_pivoted_init.index:
value=df_pivoted_init.at[index,col]
if value!=0:
insert_sql=insert_sql+"('%s','%s',%s)" %(index,col,value)+','
insert_sql = insert_sql.strip(',')
global host, port, user, passwd, db, charset
conn_config = {"host": host, "port": port, "user": user, "passwd": passwd, "db": db, "charset": charset}
conn = MySQLdb.connect(**conn_config)
cur=conn.cursor()
cur.execute("create table if not exists test_unpivot like TEST")
cur.execute(insert_sql)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def save_to_mysql(df_pivoted,tablename):
global host, port, user, passwd, db, charset
"""
只有使用sqllite时才能指定con=connection实例,其他数据库需要使用sqlalchemy生成engine,engine的定义可以添加?来设置字符集和其他属性
"""
conn="mysql://%s:%s@%s:%d/%s?charset=%s" %(user,passwd,host,port,db,charset)
mysql_engine = create_engine(conn)
df_pivoted.to_sql(name=tablename, con=mysql_engine, if_exists='replace', index=False)
# 从TEST表读取源数据至DataFrame结构
result_df=get_df()
# 将源数据行转列为二维表格形式
df_pivoted_init,df_pivoted=pivot(result_df)
# 将二维表格形式的数据存到新表test中
save_to_mysql(df_pivoted,'test')
# 将被行转列的数据unpivot,存入test_unpivot表中
unpivot(df_pivoted_init)
结果如下:
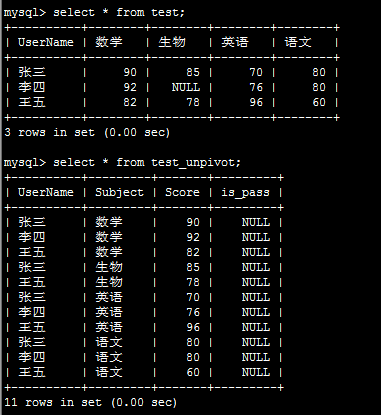
关于Pandas DataFrame类自带的pivot方法:
DataFrame.pivot(index=None, columns=None, values=None):
Return reshaped DataFrame organized by given index / column values.
这里只有3个参数,是因为pivot之后的结果一定是二维表格,只需要行列及其对应的值,而且也因为是二维表格,unpivot之后is_pass列是肯定会丢失的,因此一开始我就没查这个列。
补充说明:
在学习到Pandas的层次化索引部分时发现了2个很有意思的函数,也可以进行行列互转,其用法如下:(很久之后我才意识到,pivot只是封装了unstack的一个快捷方式而已,其本质上还是先用set_index建立层次化索引,然后用unstack进行重塑,就像我在下面示例做的操作)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
import MySQLdb
from warnings import filterwarnings
# 由于create table if not exists总会抛出warning,因此使用filterwarnings消除
filterwarnings('ignore', category = MySQLdb.Warning)
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import sys
if sys.version_info.major<3:
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")
# 此脚本适用于python2和python3
host,port,user,passwd,db,charset="192.168.1.193",3306,"leo","mysql","test","utf8"
def get_df():
global host,port,user,passwd,db,charset
conn_config={"host":host, "port":port, "user":user, "passwd":passwd, "db":db,"charset":charset}
conn = MySQLdb.connect(**conn_config)
result_df=pd.read_sql('select UserName,Subject,Score from TEST',conn)
return result_df
def pivot(result_df):
df_pivoted_init=result_df.pivot('UserName','Subject','Score')
df_pivoted = df_pivoted_init.reset_index() # 将行索引也作为DataFrame值的一部分,以方便存储数据库
return df_pivoted_init,df_pivoted
# 返回的两个DataFrame,一个是以姓名作index的,一个是以数字序列作index,前者用于unpivot,后者用于save_to_mysql
def unpivot(df_pivoted_init):
# unpivot需要进行df_pivoted_init二维表格的行、列索引遍历,需要拼SQL因此不能使用save_to_mysql存数据,这里使用SQL和MySQLdb接口存
insert_sql="insert into test_unpivot(UserName,Subject,Score) values "
# 处理值为NaN的情况
df_pivoted_init=df_pivoted_init.fillna(0)
for col in df_pivoted_init.columns:
for index in df_pivoted_init.index:
value=df_pivoted_init.at[index,col]
if value!=0:
insert_sql=insert_sql+"('%s','%s',%s)" %(index,col,value)+','
insert_sql = insert_sql.strip(',')
global host, port, user, passwd, db, charset
conn_config = {"host": host, "port": port, "user": user, "passwd": passwd, "db": db, "charset": charset}
conn = MySQLdb.connect(**conn_config)
cur=conn.cursor()
cur.execute("create table if not exists test_unpivot like TEST")
cur.execute(insert_sql)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def save_to_mysql(df_pivoted,tablename):
global host, port, user, passwd, db, charset
"""
只有使用sqllite时才能指定con=connection实例,其他数据库需要使用sqlalchemy生成engine,engine的定义可以添加?来设置字符集和其他属性
"""
conn="mysql://%s:%s@%s:%d/%s?charset=%s" %(user,passwd,host,port,db,charset)
mysql_engine = create_engine(conn)
df_pivoted.to_sql(name=tablename, con=mysql_engine, if_exists='replace', index=False)
# 从TEST表读取源数据至DataFrame结构
result_df=get_df()
# 将源数据行转列为二维表格形式
df_pivoted_init,df_pivoted=pivot(result_df)
# 将二维表格形式的数据存到新表test中
save_to_mysql(df_pivoted,'test')
# 将被行转列的数据unpivot,存入test_unpivot表中
unpivot(df_pivoted_init)
以上利用了Pandas的层次化索引,实际上这也是层次化索引一个主要的用途,结合本例我们可以把代码改成如下:
result_df=pd.read_sql('select UserName,Subject,Score from TEST',conn)
# 在从数据库中获取的数据格式是这样的:
UserName Subject Score
0 张三 语文 80.0
1 张三 数学 90.0
2 张三 英语 70.0
3 张三 生物 85.0
4 李四 语文 80.0
5 李四 数学 92.0
6 李四 英语 76.0
7 王五 语文 60.0
8 王五 数学 82.0
9 王五 英语 96.0
10 王五 生物 78.0
# 如果要使用层次化索引,那么我们只需要把UserName和Subject列设置为层次化索引,Score为其对应的值即可,我们借用set_index()函数:
df=result_df.set_index(['UserName','Subject'])
In [112]: df.unstack()
Out[112]:
Score
Subject 数学 生物 英语 语文
UserName
张三 90.0 85.0 70.0 80.0
李四 92.0 NaN 76.0 80.0
王五 82.0 78.0 96.0 60.0
# 使用stack可以将unstack的结果转回来,这样就也在形式上实现了行列互转,之后的操作基本一致了。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。