如何利用Python模拟GitHub登录详解
前言
最近学习了Fiddler抓包工具的简单使用,通过抓包,我们可以抓取到HTTP请求,并对其进行分析。现在我准备尝试着结合Python来模拟GitHub登录。
Fiddler抓包分析
首先,我们想要模拟一个网站的登录,我们必须要简单了解其大致过程。
在这里,我通过Fiddler来抓取GitHub登录的请求,从网页上登录的URL为:https://github.com/login ,抓包结果如下:
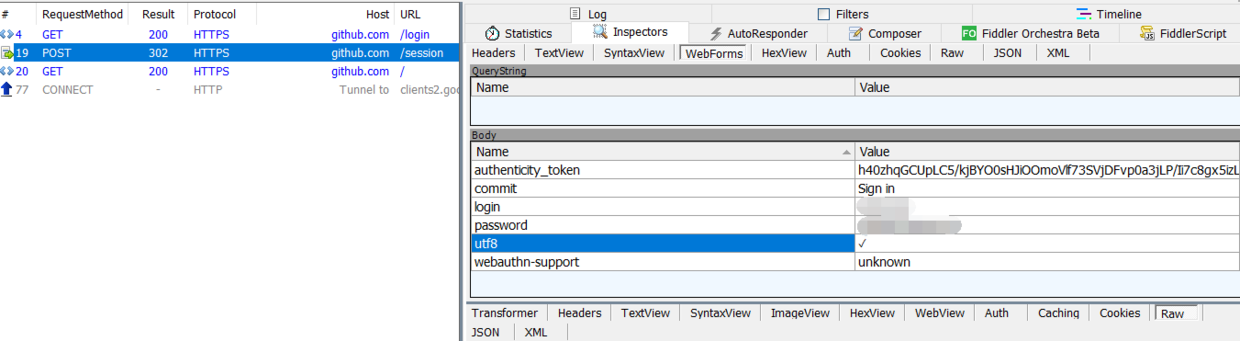
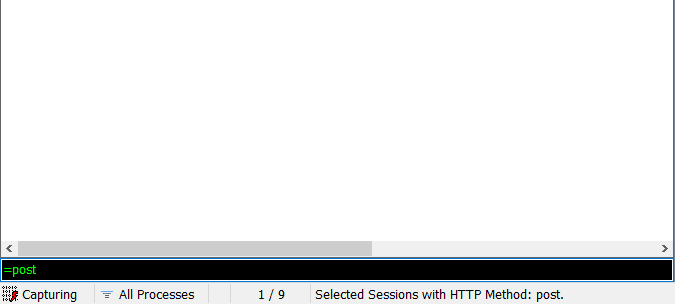
左边的是会话列表,右边的是请求和响应的数据。一般情况下,登录都是用POST请求,因为我在左边的会话列表中设置了显示RequestMethod一列,因此能够很方便的找到POST请求。当然,Fiddler默认不显示RequestMethod,如果没有设置,还可以通过命令“=post”来快速过滤POST请求。
在GitHub登录时,我们通过抓包发现,GitHub登录的URL虽然时https://github.com/login,但发生了302重定向,其真正提交POST表单数据的URL是 https://github.com/session ,当登录成功时,则会跳转到 https://github.com/ 首页。
打开WebForm,我们可以看到POST表单数据提交的值,可以发现,只有authenticity_token、login、password三个字段是会变化的,其余的每次登录都是固定的值。而login、password分别是我们登录的用户和密码,因此我们只需要分析出 authenticity_token 从何而来,便可以实现模拟登录了。
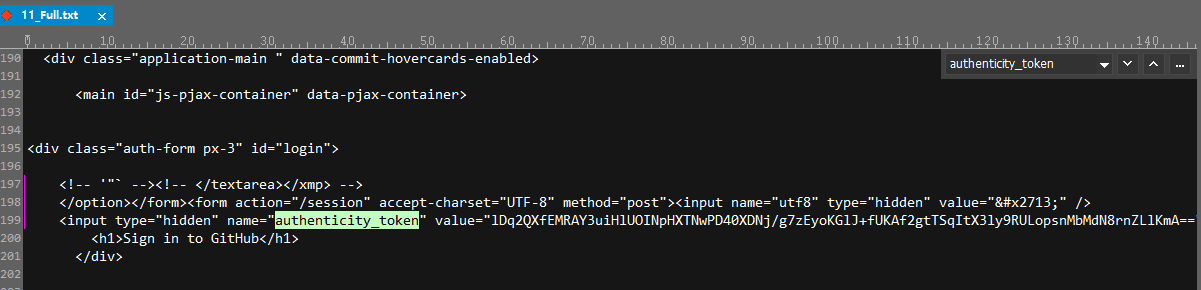
至于如何确定 authenticity_token 从哪个页面返回的,我们直接在响应数据中搜索就行了,或者把数据复制出来再进行搜索。最后我们会发现,authenticity_token 是在 https://github.com/login 这个请求中返回的,只不过用 hidden 隐藏起来了。
好了,到目前大致流程我们已经梳理清楚了,接下来我们便通过Python来实现模拟GitHub登录。
代码实现
本人环境:PyCharm 2018.2.4、Python3.7.0
1. 设置请求头和Session
# 设置Session
self.s = requests.session()
# 设置请求头
self.headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:44.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/44.0"
}
# 在使用Fiddler时进行请求,通过该代码忽略SSLError错误
self.s.verify = False
在这里,我们设置了Session会话对象,Session相当于1个微型浏览器,能够自动帮我们保持请求中的某些参数(如cookies),有了它,我们一般不需要额外去处理cookies、header等。
假如我们是在Fiddler打开的状态下,通过代码进行请求,那么将会遇到SSLError的错误,而当加上 self.s.verify = False 这行代码后,我们便可以忽略该错误。
requests.exceptions.SSLError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='github.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /login (Caused by SSLError(SSLCertVerificationError(1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: unable to get local issuer certificate (_ssl.c:1045)')))
注意:
我们通过上面的代码忽略了SSLError的错误后,再次运行,这时仍然会出现2行警告,这2个警告并不影响我们的登录,可以不管它。
D:\Python\installation\lib\site-packages\urllib3\connectionpool.py:847: InsecureRequestWarning: Unverified HTTPS request is being made. Adding certificate verification is strongly advised. See: https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced-usage.html#ssl-warnings InsecureRequestWarning) D:\Python\installation\lib\site-packages\urllib3\connectionpool.py:847: InsecureRequestWarning: Unverified HTTPS request is being made. Adding certificate verification is strongly advised. See: https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced-usage.html#ssl-warnings InsecureRequestWarning)
如果我们想去掉这2行警告,也可以通过如下代码来解决(针对Python3):
import urllib3 urllib3.disable_warnings()
2. 获取authenticity_token
login_url = "https://github.com/login"
r = self.s.get(login_url, headers = self.headers)
authenticity_token = re.findall('<input type="hidden" name="authenticity_token" value="(.+?)" />', r.text)
print("authenticity_token:{}".format(authenticity_token))
return authenticity_token[1]
当我们访问 https://github.com/login 时,登录界面会生成隐藏参数authenticity_token,而这恰是我们在登录提交表单时需要用到的参数。我们可通过正则表达式 re.findall 来获取authenticity_token。另外,我们还会发现,HTML界面中存在2个authenticity_token,因此通过正则返回的是一个长度为2的列表,经过分析,GitHub在登录时用到的是列表中的第二个元素,即authenticity_token[1]。
3. 模拟登录
def github_login(self, authenticity_token, username, password):
session_url = "https://github.com/session"
body = {
"authenticity_token":authenticity_token,
"commit":"Sign in",
"login":username,
"password":password,
"utf8":"✓",
"webauthn-support":"unknown"
}
r = self.s.post(session_url, headers = self.headers, data = body)
title = re.findall('<title>(.+?)</title>',r.text)
print("title:%s" %title[0])
return title[0]
我们在上面得到authenticity_token后,便可以来实现登录了。通过POST请求提交表单后,我们需要判断是否登录成功。在这里,我是通过页面的标题来判断GitHub是否登录成功,当然,还有许多方法可以用于判断。
4. 通过 title 判断是否登录成功
def is_login_success(self, title):
if "GitHub" == title:
return True
else:
return False
GitHub登录成功后,界面的标题会显示"GitHub",而登录失败时,一般显示的标题则是"Sign in to GitHub · GitHub"。
OK,以上就是通过Python模拟GitHub登录的过程,难度不大,相信大多数人阅读后都应该可以进行实践。
附源码:
import requests
import re
import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings()
class Github_Login():
def __init__(self):
# 设置Session
self.s = requests.session()
# 设置请求头
self.headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:44.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/44.0"
}
# 在使用Fiddler时进行请求,通过该代码忽略SSLError错误
self.s.verify = False
# 获取 authenticity_token
def get_authenticity_token(self):
login_url = "https://github.com/login"
r = self.s.get(login_url, headers = self.headers)
authenticity_token = re.findall('<input type="hidden" name="authenticity_token" value="(.+?)" />', r.text)
print("authenticity_token:{}".format(authenticity_token))
return authenticity_token[1]
# 模拟登录,并返回 title
def github_login(self, authenticity_token, username, password):
session_url = "https://github.com/session"
body = {
"authenticity_token":authenticity_token,
"commit":"Sign in",
"login":username,
"password":password,
"utf8":"✓",
"webauthn-support":"unknown"
}
r = self.s.post(session_url, headers = self.headers, data = body)
title = re.findall('<title>(.+?)</title>',r.text)
print("title:%s" %title[0])
return title[0]
# 通过 title 判断是否登录成功
def is_login_success(self, title):
if "GitHub" == title:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
github = Github_Login()
authenticity_token = github.get_authenticity_token()
title = github.github_login(authenticity_token, username = "用户名", password = "密码")
login_result = github.is_login_success(title)
print(login_result)
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对【听图阁-专注于Python设计】的支持。