Django 自定义分页器的实现代码
为什么要实现分页?
在大部分网站中分页的功能都是必要的,尤其是在后台管理中分页更是不可或缺
分页能带给用户更好的体验,也能减轻服务器的压力
对于分页来说,有许多方法都可以实现
例如把数据全部读取出来在前端用javascript实现,但这样一次请求全部数据服务器压力很大,
还有就是在后端实现,每一次请求部分数据显示
分页需求:
1. 每页显示的多少条数据
2. 页面显示多少个页码
3. 上一页和下一页
4. 首页和尾页
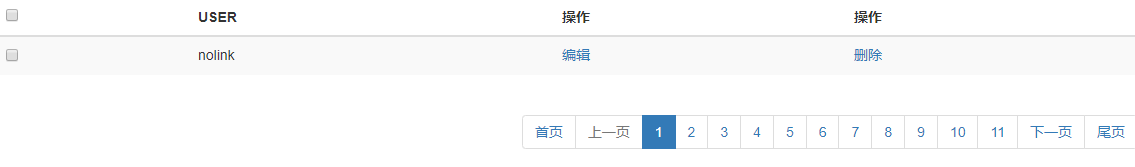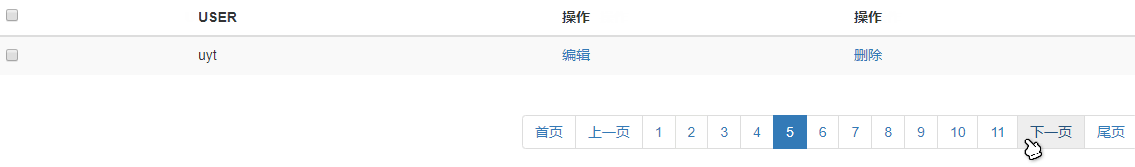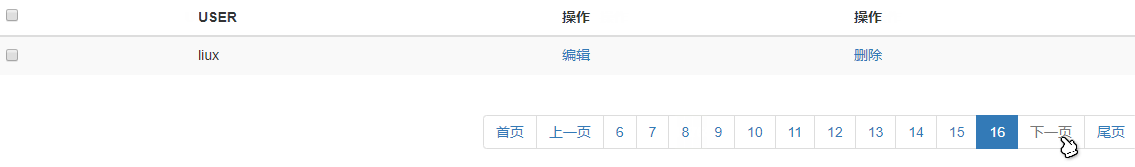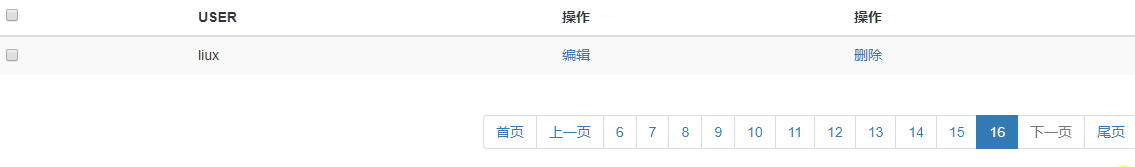
效果演示:
代码实现:
分页类封装:
在我的app下创建一个page.py文件,进行封装,我是先在我的app下创建了一个utils文件再创建page.py

class Pagination(object):
def __init__(self, current_page_num, all_count, request, per_page_num=10, pager_count=11):
"""
封装分页相关数据
:param current_page_num: 当前访问页的数字
:param all_count: 分页数据中的数据总条数
:param per_page_num: 每页显示的数据条数
:param pager_count: 最多显示的页码个数
"""
try:
current_page_num = int(current_page_num)
except Exception as e:
current_page_num = 1
if current_page_num < 1:
current_page_num = 1
self.current_page_num = current_page_num
self.all_count = all_count
self.per_page_num = per_page_num
# 实际总页码
all_pager, tmp = divmod(all_count, per_page_num)
if tmp:
all_pager += 1
self.all_pager = all_pager
self.pager_count = pager_count
self.pager_count_half = int((pager_count - 1) / 2) # 5
# 保存搜索条件
import copy
self.params = copy.deepcopy(request.GET) # {"a":"1","b":"2"}
# 开始
@property
def start(self):
return (self.current_page_num - 1) * self.per_page_num
# 结束
@property
def end(self):
return self.current_page_num * self.per_page_num
# 实现
def page_html(self):
# 如果总页码 < 11个:
if self.all_pager <= self.pager_count:
pager_start = 1
pager_end = self.all_pager + 1
# 总页码 > 11
else:
# 当前页如果<=页面上最多显示11/2个页码
if self.current_page_num <= self.pager_count_half:
pager_start = 1
pager_end = self.pager_count + 1
# 当前页大于5
else:
# 页码翻到最后
if (self.current_page_num + self.pager_count_half) > self.all_pager:
pager_start = self.all_pager - self.pager_count + 1
pager_end = self.all_pager + 1
else:
pager_start = self.current_page_num - self.pager_count_half
pager_end = self.current_page_num + self.pager_count_half + 1
page_html_list = []
first_page = '<li><a href="?page=%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >首页</a></li>' % (1,)
page_html_list.append(first_page)
if self.current_page_num <= 1:
prev_page = '<li class="disabled"><a href="#" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >上一页</a></li>'
else:
prev_page = '<li><a href="?page=%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >上一页</a></li>' % (self.current_page_num - 1,)
page_html_list.append(prev_page)
# self.params=copy.deepcopy(request.GET) # {"a":"1","b":"2"}
for i in range(pager_start, pager_end):
self.params["page"] = i
if i == self.current_page_num:
temp = '<li class="active"><a href="?%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >%s</a></li>' % (self.params.urlencode(), i)
else:
temp = '<li><a href="?%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >%s</a></li>' % (self.params.urlencode(), i,)
page_html_list.append(temp)
if self.current_page_num >= self.all_pager:
next_page = '<li class="disabled"><a href="#" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >下一页</a></li>'
else:
next_page = '<li><a href="?page=%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >下一页</a></li>' % (self.current_page_num + 1,)
page_html_list.append(next_page)
last_page = '<li><a href="?page=%s" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >尾页</a></li>' % (self.all_pager,)
page_html_list.append(last_page)
return ''.join(page_html_list)
在视图中使用
views.py
# 首先导入包
from myapp.utils.page import Pagination
from myapp.models import User
def index(request):
# queryset
user_list = User.objects.all()
# 总页数
page_count = user_list.count()
# 当前页
current_page_num = request.GET.get("page")
pagination = Pagination(current_page_num, page_count, request, per_page_num=1)
# 处理之后的数据
user_list = user_list[pagination.start:pagination.end]
content = {
"user_list": user_list,
"pagination": pagination,
}
return render(request, "user_list.html", content)
页面显示
user_list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="external nofollow" >
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>name</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for user in user_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ user.name }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<!-- bootstrap 样式 -->
<div class="dataTables_paginate paging_simple_numbers pull-right">
<ul class="pagination">
{{ pagination.page_html|safe }}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。