TensorFlow——Checkpoint为模型添加检查点的实例
1.检查点
保存模型并不限于在训练模型后,在训练模型之中也需要保存,因为TensorFlow训练模型时难免会出现中断的情况,我们自然希望能够将训练得到的参数保存下来,否则下次又要重新训练。
这种在训练中保存模型,习惯上称之为保存检查点。
2.添加保存点
通过添加检查点,可以生成载入检查点文件,并能够指定生成检查文件的个数,例如使用saver的另一个参数——max_to_keep=1,表明最多只保存一个检查点文件,在保存时使用如下的代码传入迭代次数。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
train_x = np.linspace(-5, 3, 50)
train_y = train_x * 5 + 10 + np.random.random(50) * 10 - 5
plt.plot(train_x, train_y, 'r.')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
tf.reset_default_graph()
X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
w = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1]), name='Weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1]), name='bias')
z = tf.multiply(X, w) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y - z))
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
training_epochs = 20
display_step = 2
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=15)
savedir = "model/"
if __name__ == '__main__':
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for (x, y) in zip(train_x, train_y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
loss_list.append(loss)
print('Iter: ', epoch, ' Loss: ', loss)
w_, b_ = sess.run([w, b], feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
saver.save(sess, savedir + "linear.cpkt", global_step=epoch)
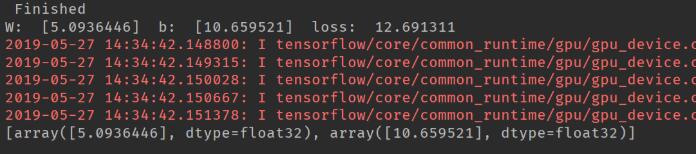
print(" Finished ")
print("W: ", w_, " b: ", b_, " loss: ", loss)
plt.plot(train_x, train_x * w_ + b_, 'g-', train_x, train_y, 'r.')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
load_epoch = 10
with tf.Session() as sess2:
sess2.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.restore(sess2, savedir + "linear.cpkt-" + str(load_epoch))
print(sess2.run([w, b], feed_dict={X: train_x, Y: train_y}))
在上述的代码中,我们使用saver.save(sess, savedir + "linear.cpkt", global_step=epoch)将训练的参数传入检查点进行保存,saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=1)表示只保存一个文件,这样在训练过程中得到的新的模型就会覆盖以前的模型。
cpkt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(savedir) if cpkt and cpkt.model_checkpoint_path: saver.restore(sess2, cpkt.model_checkpoint_path) kpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(savedir) saver.restore(sess2, kpt)
上述的两种方法也可以对checkpoint文件进行加载,tf.train.latest_checkpoint(savedir)为加载最后的检查点文件。这种方式,我们可以通过保存指定训练次数的检查点,比如保存5的倍数次保存一下检查点。
3.简便保存检查点
我们还可以用更加简单的方法进行检查点的保存,tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession()函数,该函数可以直接实现保存载入检查点模型的文件,与前面的方法不同的是,它是按照训练时间来保存检查点的,可以通过指定save_checkpoint_secs参数的具体秒数,设置多久保存一次检查点。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
train_x = np.linspace(-5, 3, 50)
train_y = train_x * 5 + 10 + np.random.random(50) * 10 - 5
# plt.plot(train_x, train_y, 'r.')
# plt.grid(True)
# plt.show()
tf.reset_default_graph()
X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
w = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1]), name='Weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1]), name='bias')
z = tf.multiply(X, w) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y - z))
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
training_epochs = 30
display_step = 2
global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
step = tf.assign_add(global_step, 1)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
savedir = "check-point/"
if __name__ == '__main__':
with tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession(checkpoint_dir=savedir + 'linear.cpkt', save_checkpoint_secs=5) as sess:
sess.run(init)
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
sess.run(global_step)
for (x, y) in zip(train_x, train_y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
loss_list.append(loss)
print('Iter: ', epoch, ' Loss: ', loss)
w_, b_ = sess.run([w, b], feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
sess.run(step)
print(" Finished ")
print("W: ", w_, " b: ", b_, " loss: ", loss)
plt.plot(train_x, train_x * w_ + b_, 'g-', train_x, train_y, 'r.')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
load_epoch = 10
with tf.Session() as sess2:
sess2.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# saver.restore(sess2, savedir + 'linear.cpkt-' + str(load_epoch))
# cpkt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(savedir)
# if cpkt and cpkt.model_checkpoint_path:
# saver.restore(sess2, cpkt.model_checkpoint_path)
#
kpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(savedir + 'linear.cpkt')
saver.restore(sess2, kpt)
print(sess2.run([w, b], feed_dict={X: train_x, Y: train_y}))
上述的代码中,我们设置了没训练了5秒中之后,就保存一次检查点,它默认的保存时间间隔是10分钟,这种按照时间的保存模式更适合使用大型数据集训练复杂模型的情况,注意在使用上述的方法时,要定义global_step变量,在训练完一个批次或者一个样本之后,要将其进行加1的操作,否则将会报错。
以上这篇TensorFlow——Checkpoint为模型添加检查点的实例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。